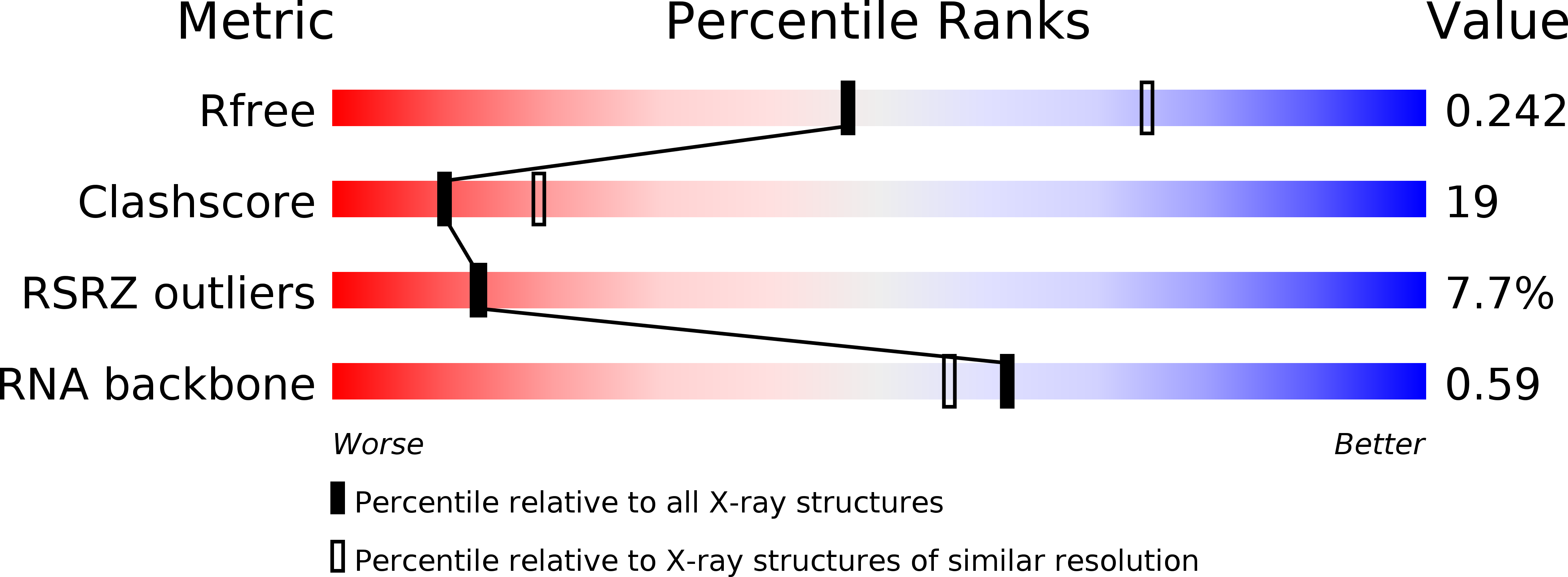
Deposition Date
2006-07-14
Release Date
2006-09-19
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2HOJ
Keywords:
Title:
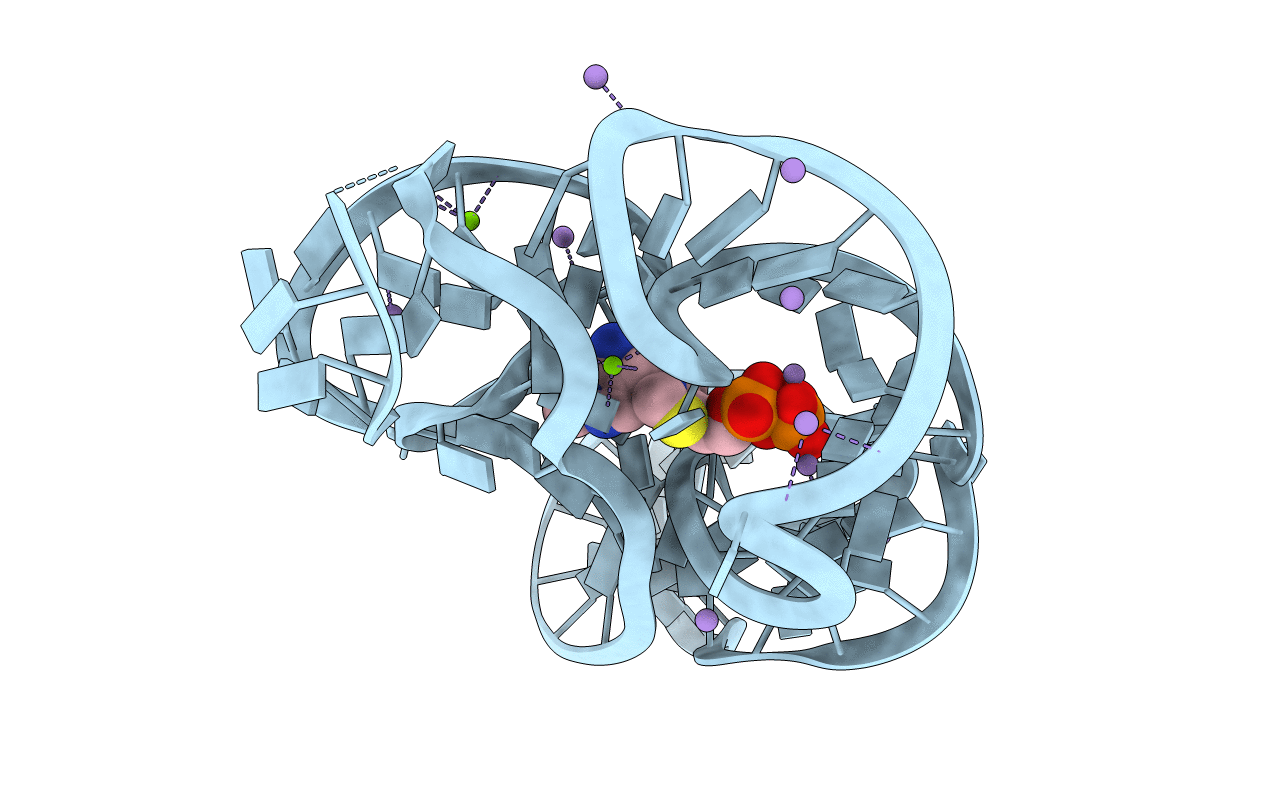
Crystal structure of an E. coli thi-box riboswitch bound to thiamine pyrophosphate, manganese ions
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
Space Group:
P 32 1 2