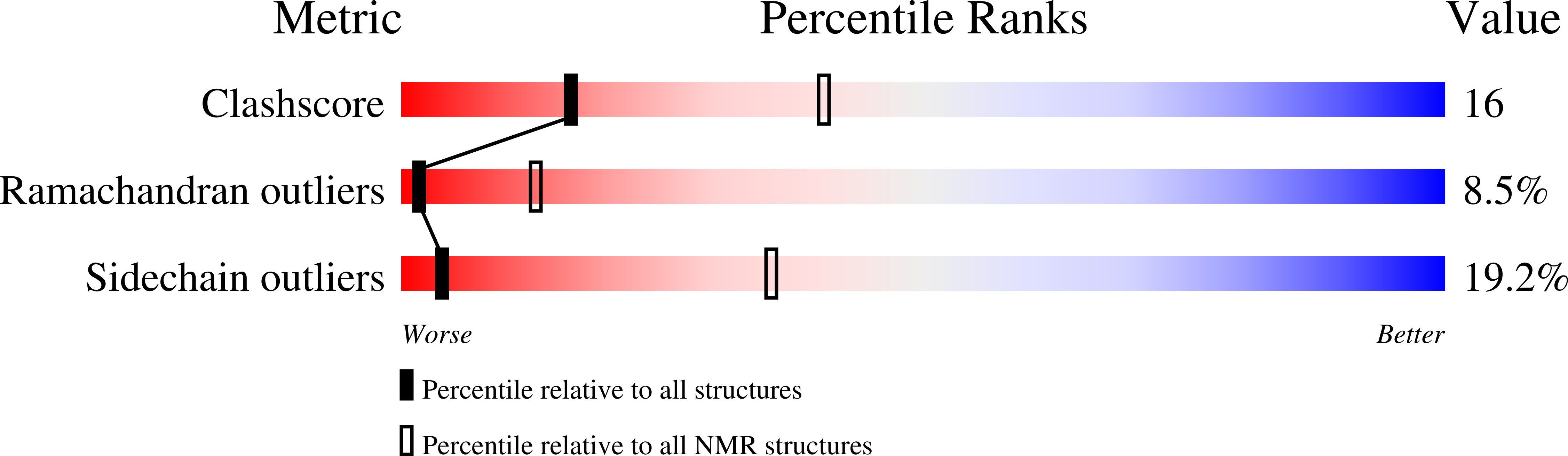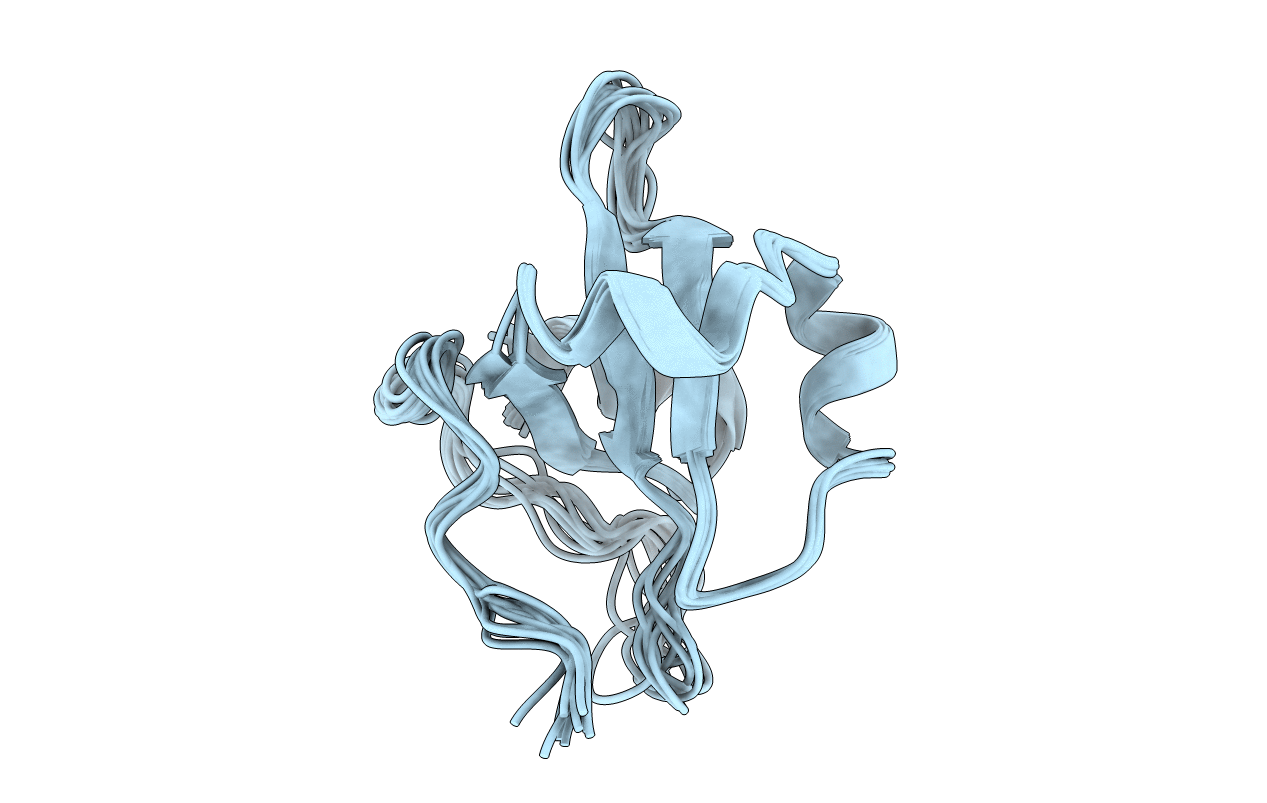
Deposition Date
2006-04-07
Release Date
2007-02-27
Last Version Date
2024-05-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2GMO
Keywords:
Title:
NMR-structure of an independently folded C-terminal domain of influenza polymerase subunit PB2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Influenza A virus (A/Victoria/3/1975(H3N2)) (Taxon ID: 392809)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
1000
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
10 structures of lowest energy