Deposition Date
2006-03-06
Release Date
2006-11-07
Last Version Date
2024-05-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2G9J
Keywords:
Title:
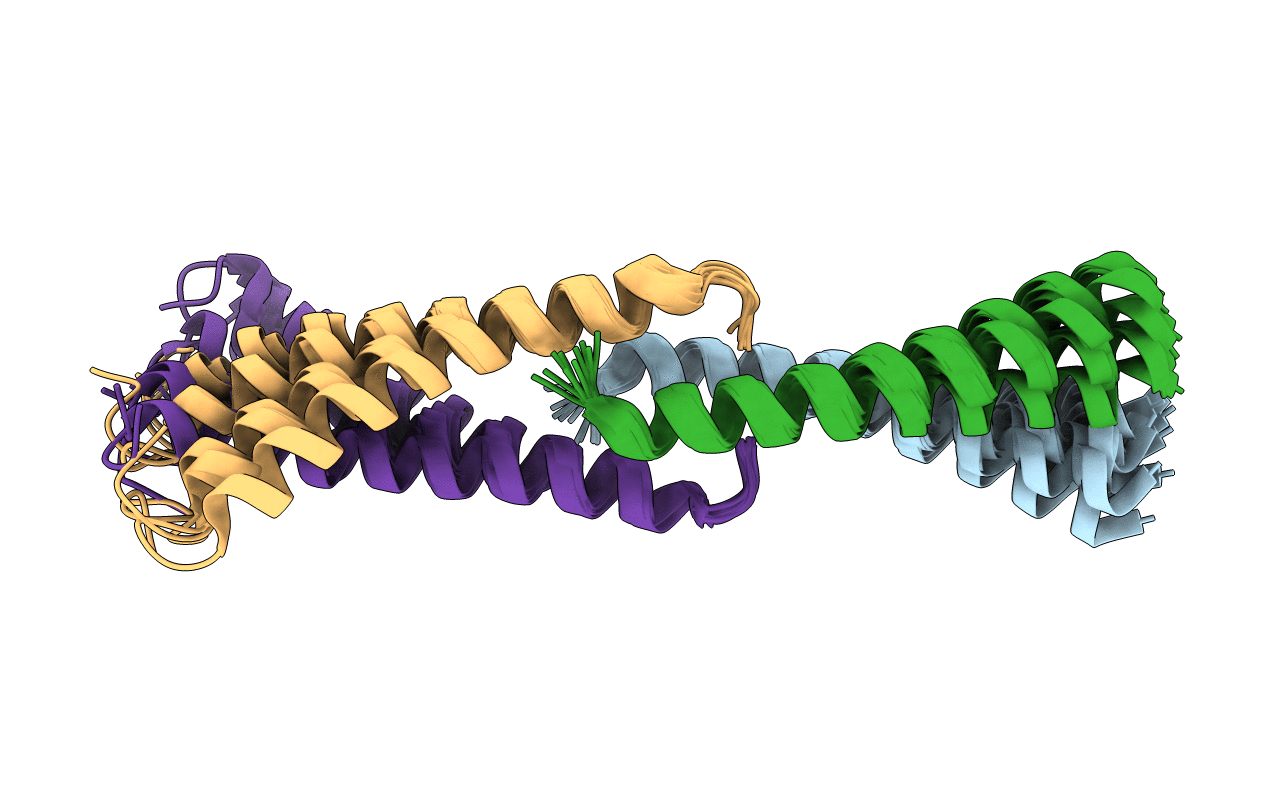
Complex of TM1a(1-14)Zip with TM9a(251-284): a model for the polymerization domain ("overlap region") of tropomyosin, Northeast Structural Genomics Target OR9
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Rattus norvegicus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 10116,4932)
Rattus norvegicus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 10116,4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
196
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
10 structures from initial DYANA calcultions with the lowest target functions were refined using CNS. The structures back calculated data agree with experimental NOESY spectra. The structures have acceptable covalent geometry, favorable non-bond energy, the lowest energy and the fewest restraint violations.


