Deposition Date
2005-12-13
Release Date
2007-01-16
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2FD9
Keywords:
Title:
X-ray Crystal Structure of Chemically Synthesized Crambin-{alpha}carboxamide
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
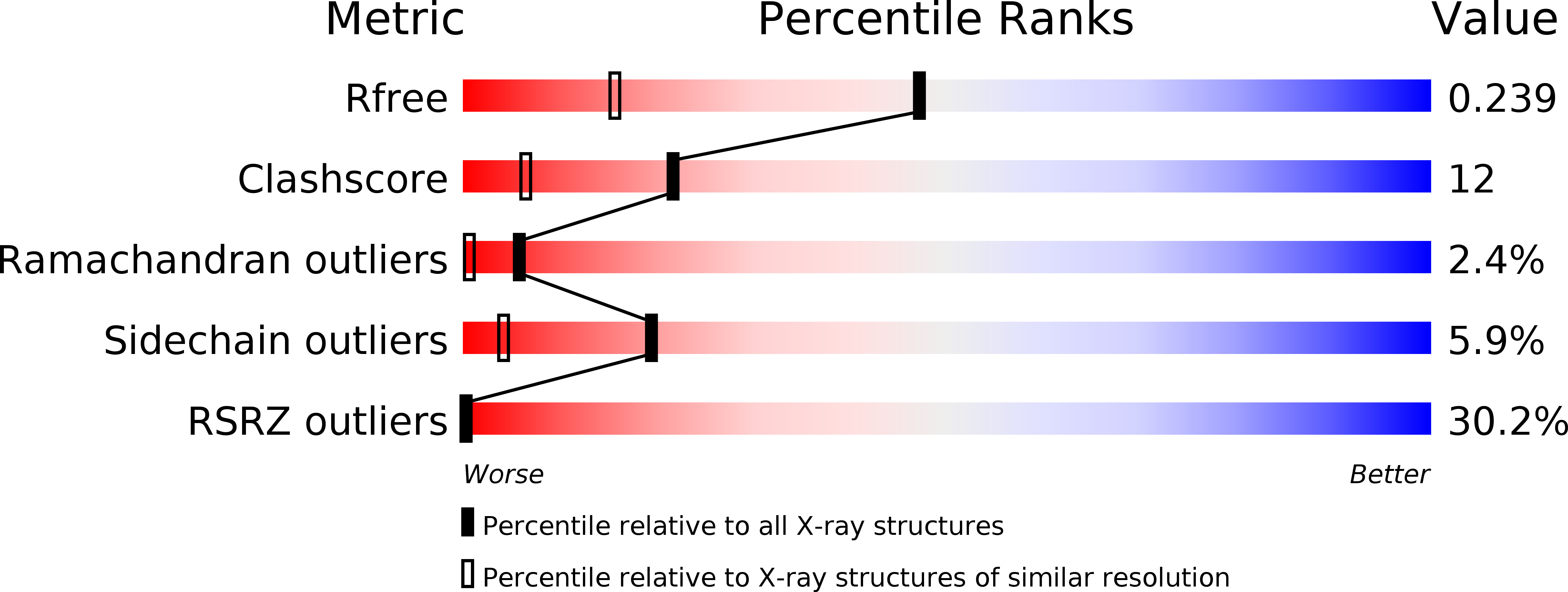
Resolution:
1.60 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
H 3 2