Deposition Date
2005-11-09
Release Date
2006-11-21
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2EYU
Keywords:
Title:
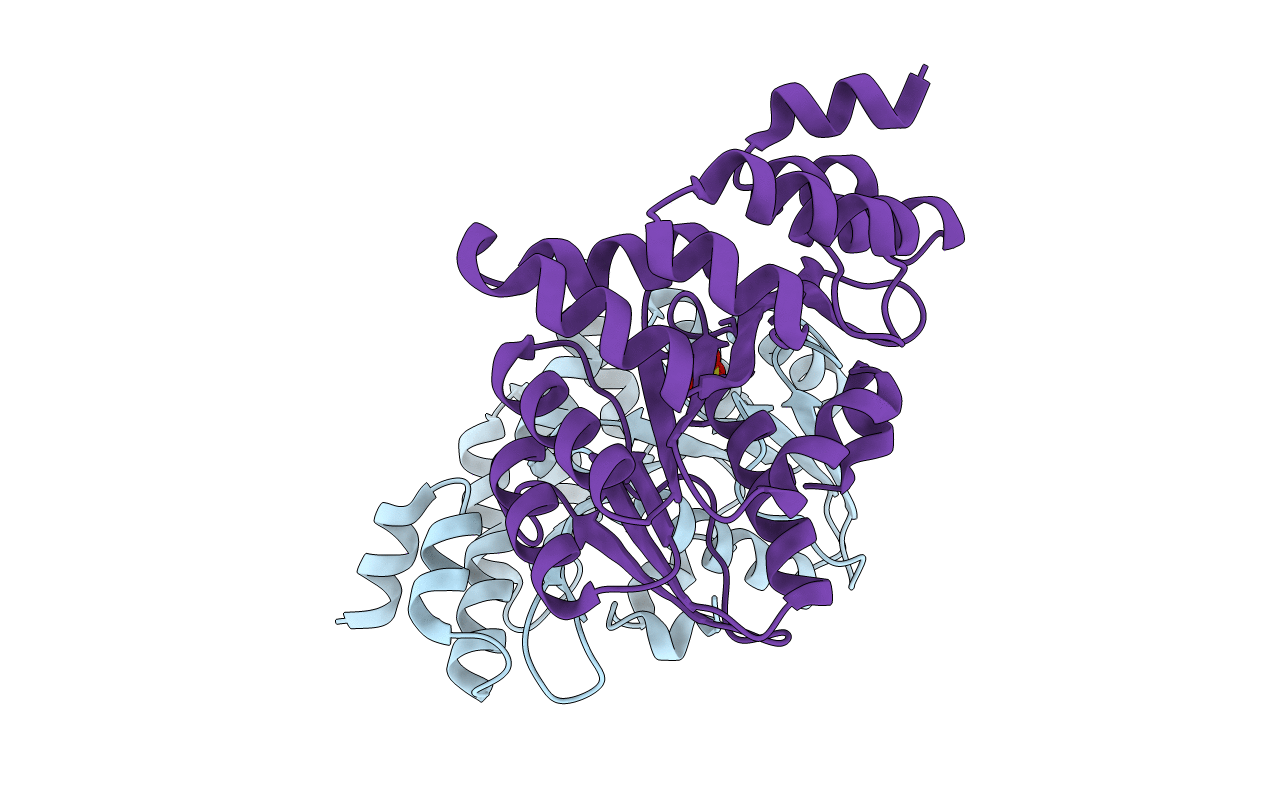
The Crystal Structure of the C-terminal Domain of Aquifex aeolicus PilT
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Aquifex aeolicus (Taxon ID: 63363)
Expression System(s):
Method Details: