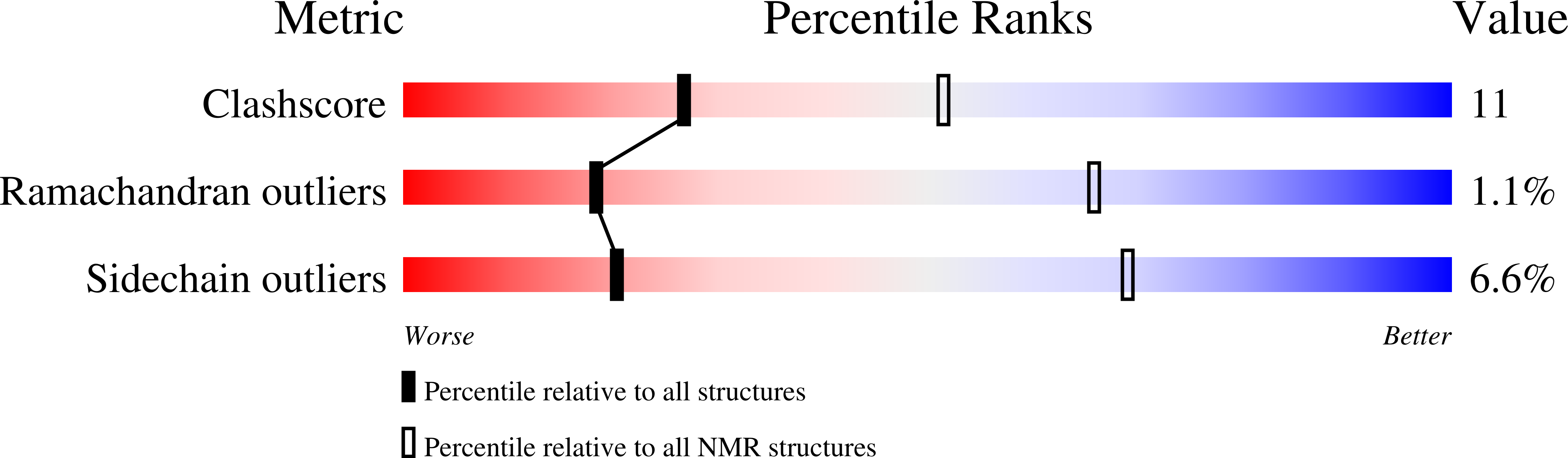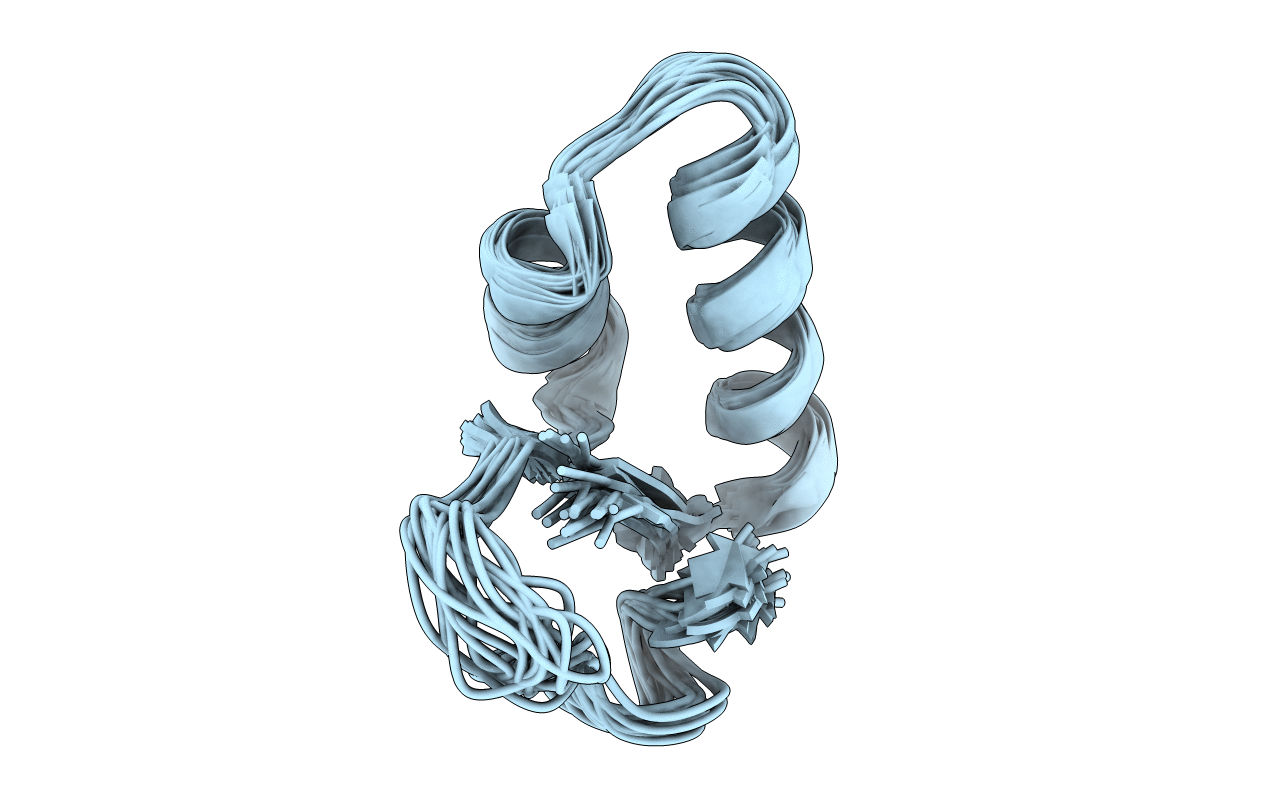
Deposition Date
2005-11-09
Release Date
2006-05-23
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2EYC
Keywords:
Title:
DMSO refined solution structure of crambin in dpc micelles
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Crambe hispanica subsp. abyssinica (Taxon ID: 3721)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
DMSO REFINED STRUCTURES WITH THE LOWEST ENERGY