Deposition Date
2006-02-08
Release Date
2006-04-10
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2CEK
Keywords:
Title:
Conformational Flexibility in the Peripheral Site of Torpedo californica Acetylcholinesterase Revealed by the Complex Structure with a Bifunctional Inhibitor
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
TORPEDO CALIFORNICA (Taxon ID: 7787)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.20 Å
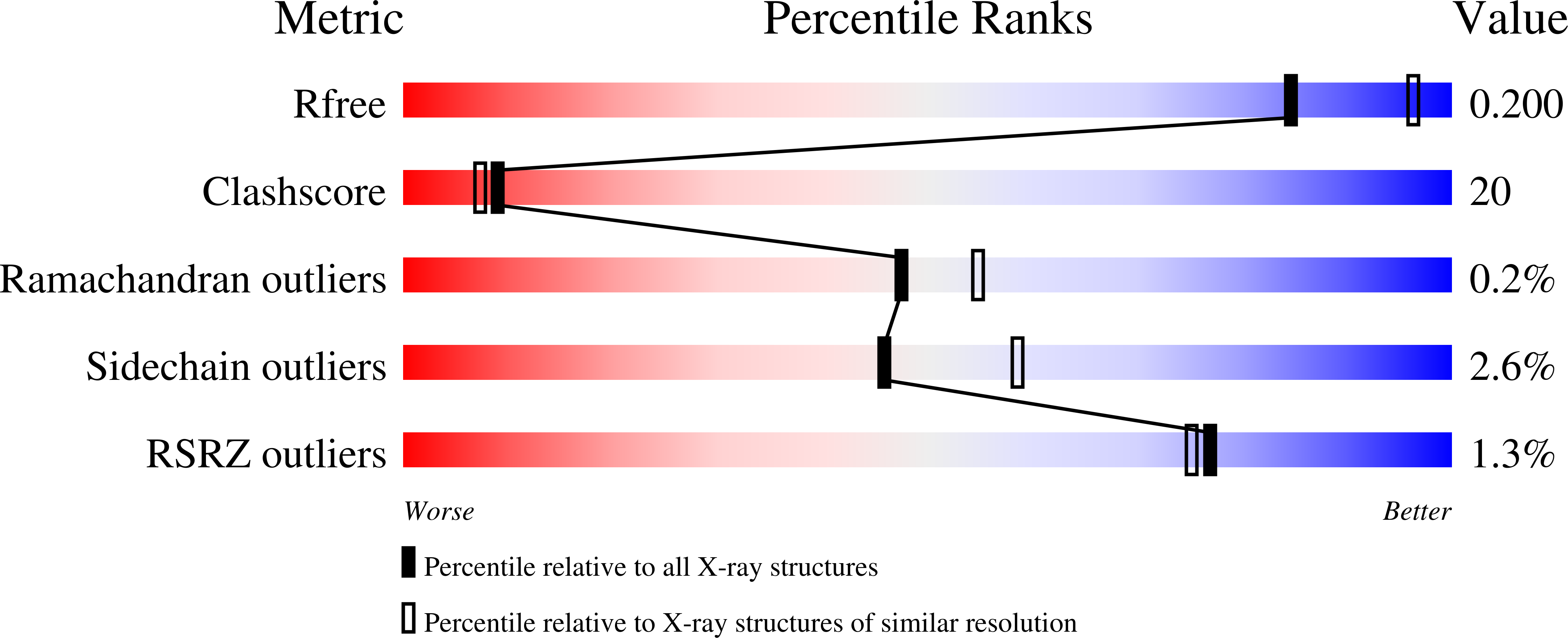
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 31 2 1