Deposition Date
2005-06-30
Release Date
2006-10-30
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2BVK
Keywords:
Title:
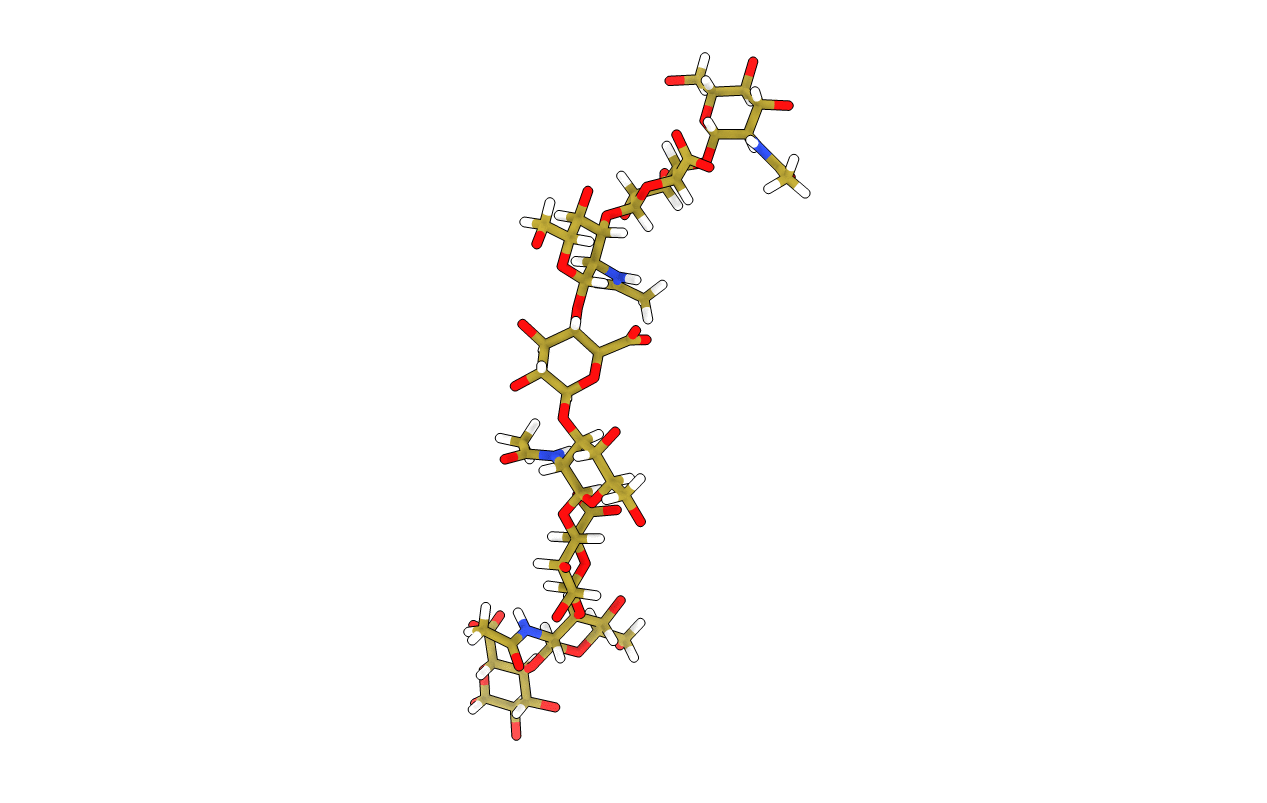
Hyaluronan: the local solution conformation determined by NMR and computer modelling is close to a contracted left-handed four-fold helix
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
250000
Conformers Submitted:
1
Selection Criteria:
AVERAGE CONFORMATION FROM A 50 NAN MOLECULAR DYNAMICS TRAJECTORY THAT EXPLICIT SOLVENT WATER AND CHARGE SODIUM IONS. THE 1-3 AND 1-4 LINKA FIXED AT (50.78, 9.78) AND (47.98, RESPECTIVELY USING THE H1-C1-OX-HX NOMENCLATURE