Deposition Date
2005-10-19
Release Date
2005-12-20
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2BCW
Keywords:
Title:
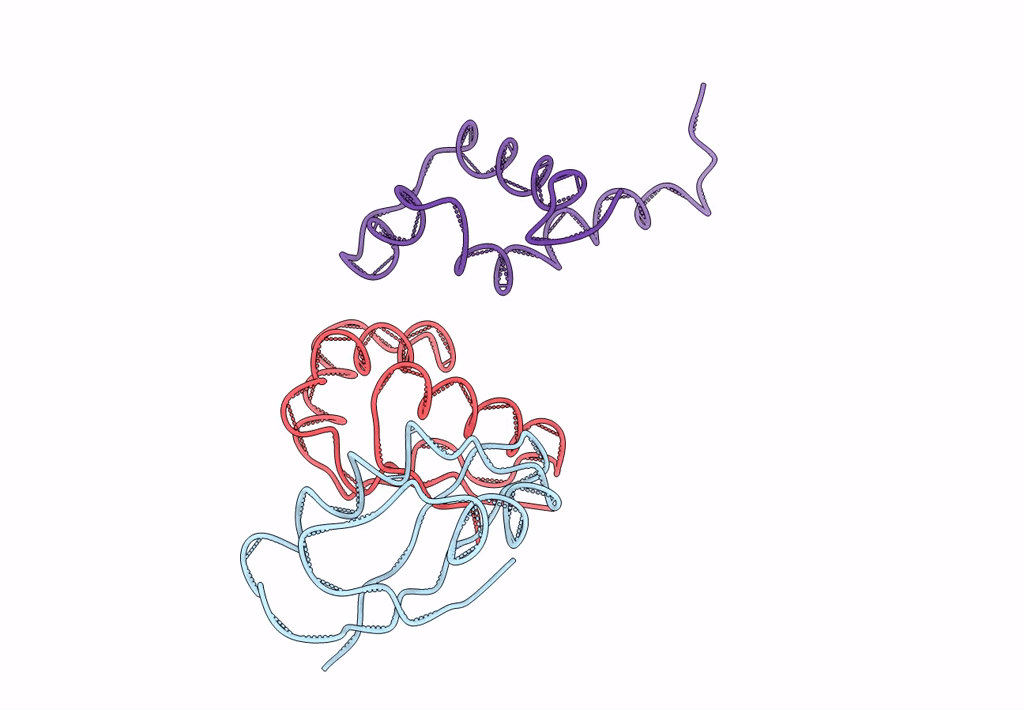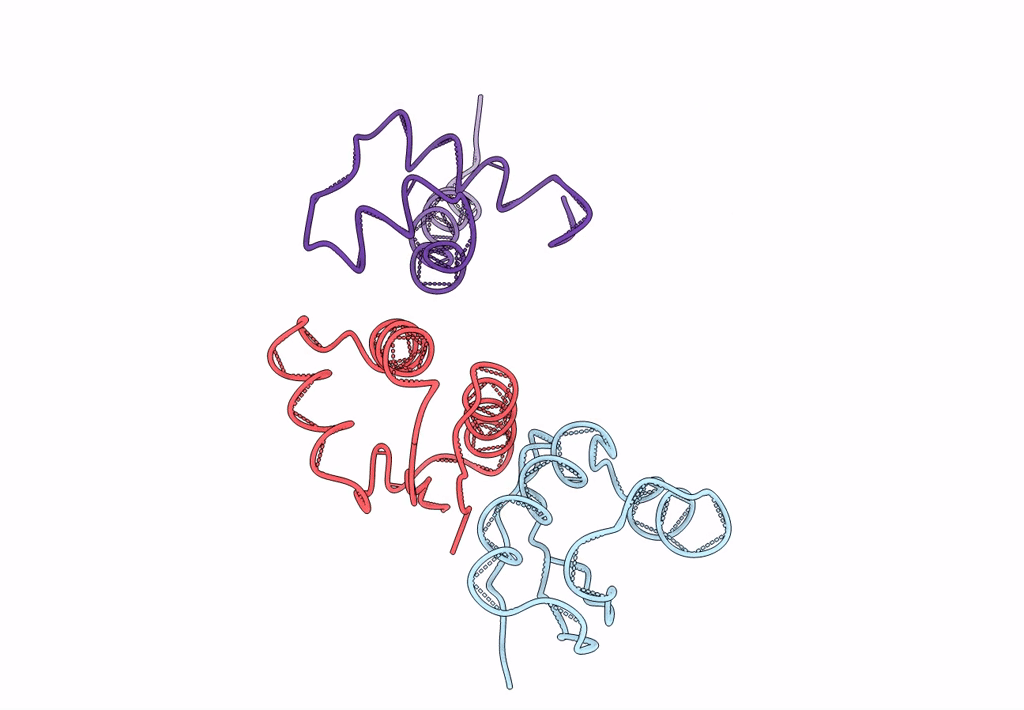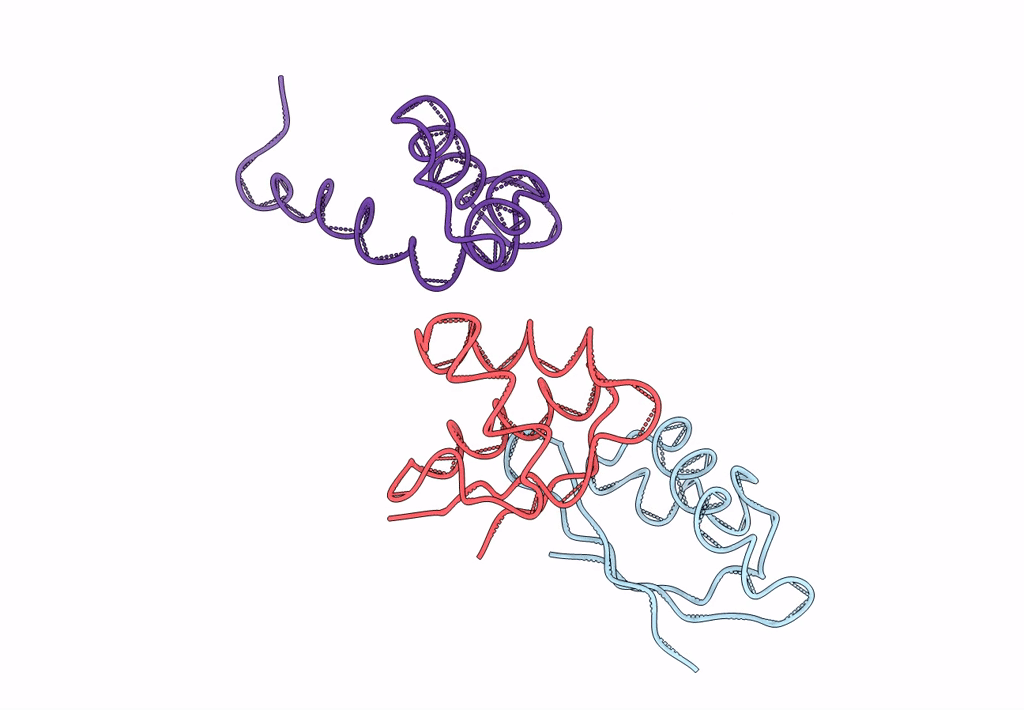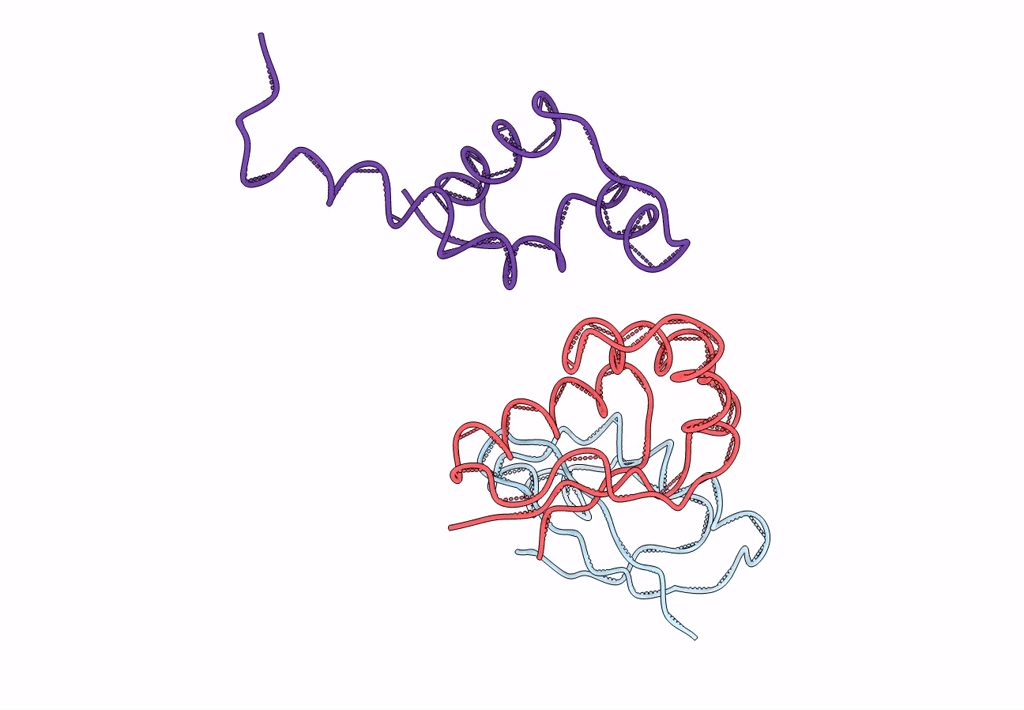
Coordinates of the N-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L11,C-terminal domain of ribosomal protein L7/L12 and a portion of the G' domain of elongation factor G, as fitted into cryo-em map of an Escherichia coli 70S*EF-G*GDP*fusidic acid complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermotoga maritima (Taxon ID: 2336)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Thermus thermophilus (Taxon ID: 274)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Thermus thermophilus (Taxon ID: 274)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
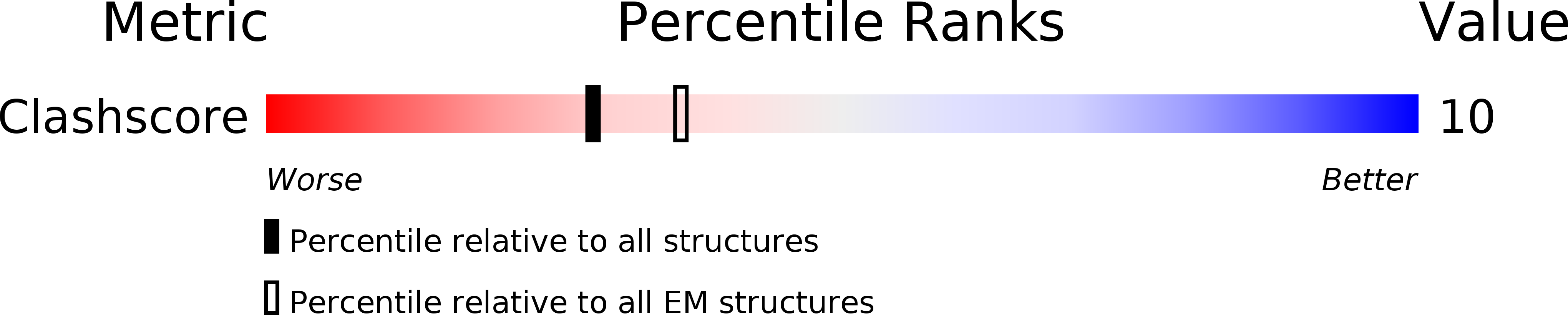
Resolution:
11.20 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE