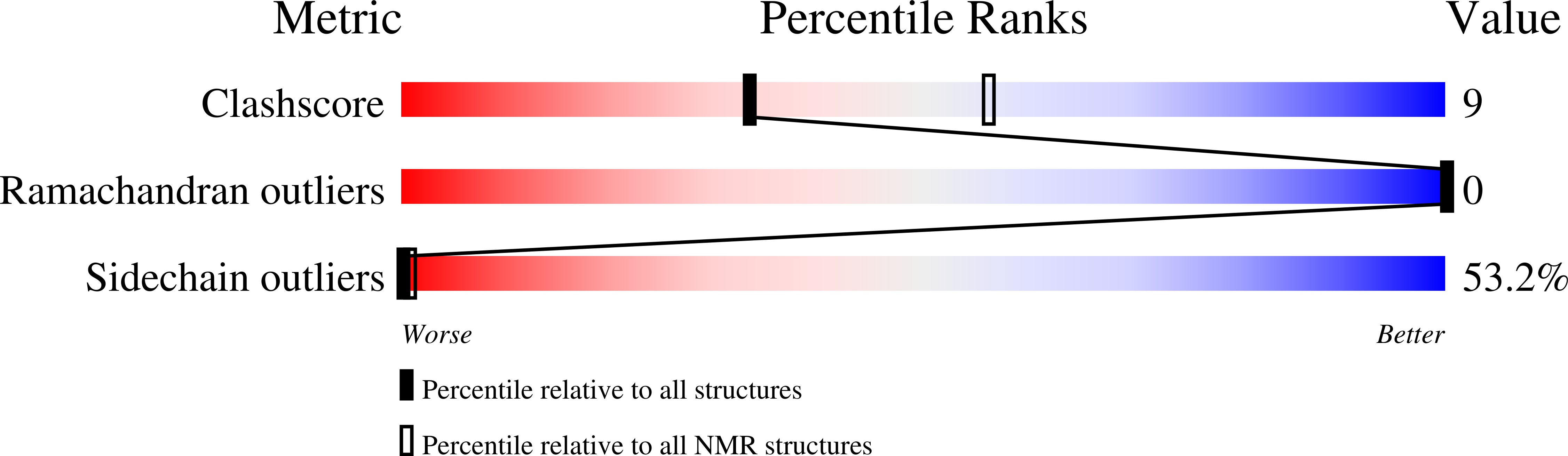
Deposition Date
2005-09-15
Release Date
2006-08-29
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2B0Y
Keywords:
Title:
Solution Structure of a peptide mimetic of the fourth cytoplasmic loop of the G-protein coupled CB1 cannabinoid receptor
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
target function