Deposition Date
2005-07-11
Release Date
2006-01-10
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2A9H
Keywords:
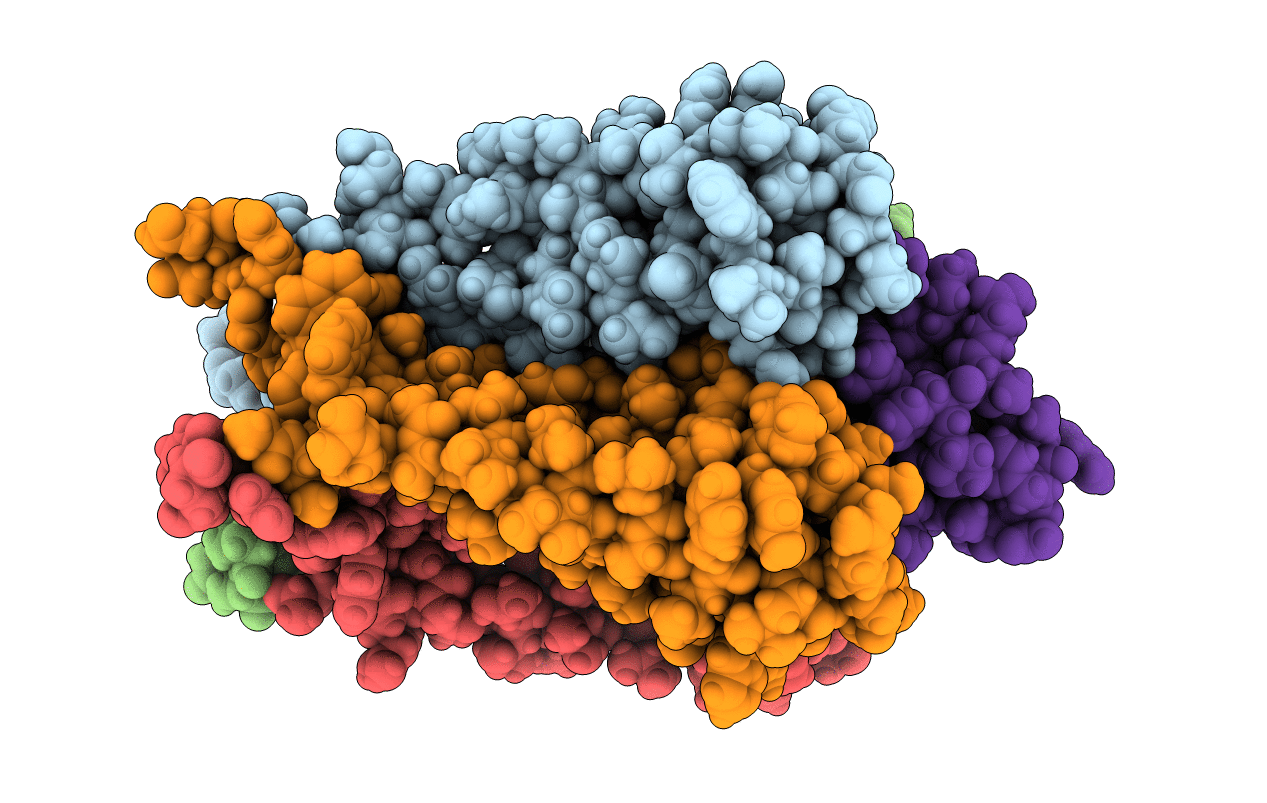
Title:
NMR structural studies of a potassium channel / charybdotoxin complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces lividans (Taxon ID: 1916)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
1


