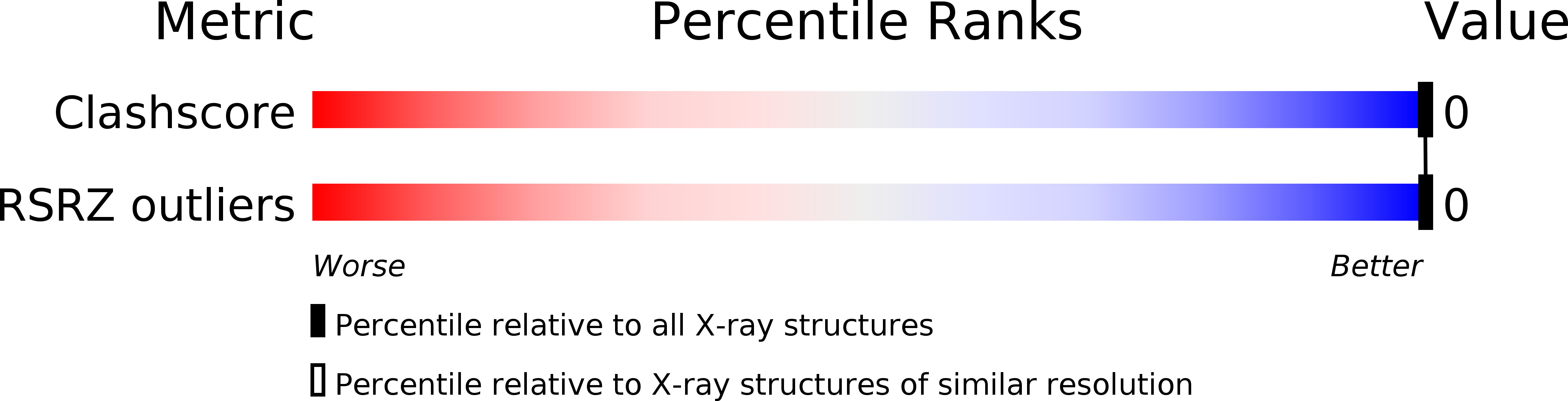
Deposition Date
1996-03-31
Release Date
1996-04-15
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
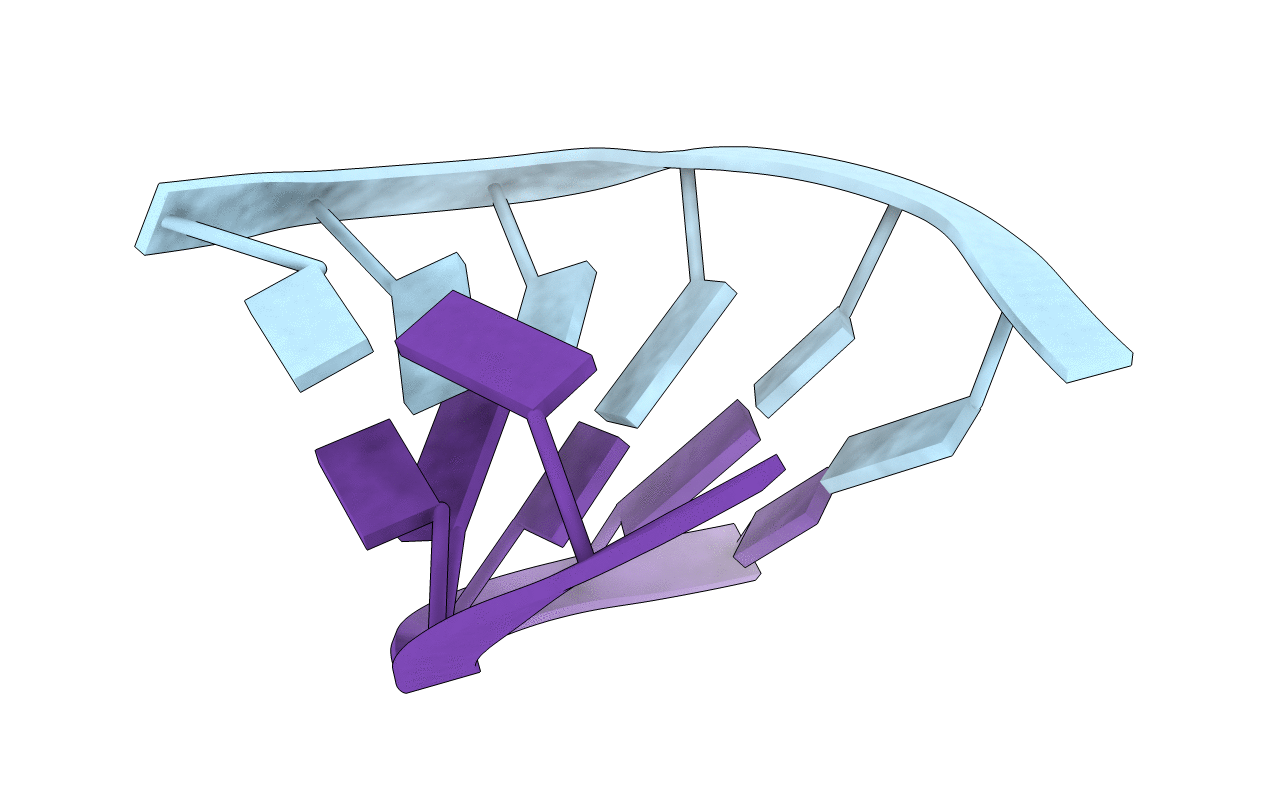
256D
Keywords:
Title:
ALTERNATING AND NON-ALTERNATING DG-DC HEXANUCLEOTIDES CRYSTALLIZE AS CANONICAL A-DNA
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
C 2 2 21