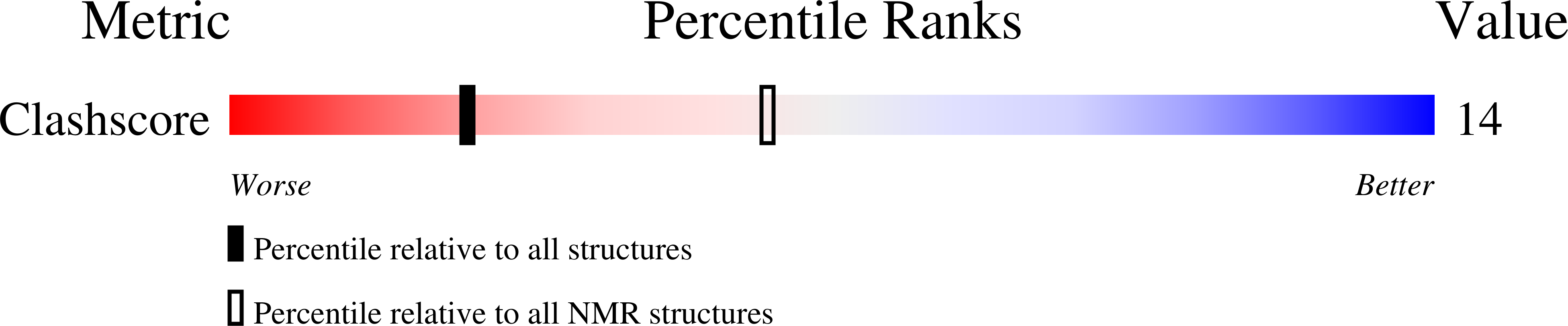
Deposition Date
1995-03-16
Release Date
1995-07-31
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
201D
Keywords:
Title:
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE OXYTRICHA TELOMERIC REPEAT D[G4(T4G4)3] G-TETRAPLEX
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
6