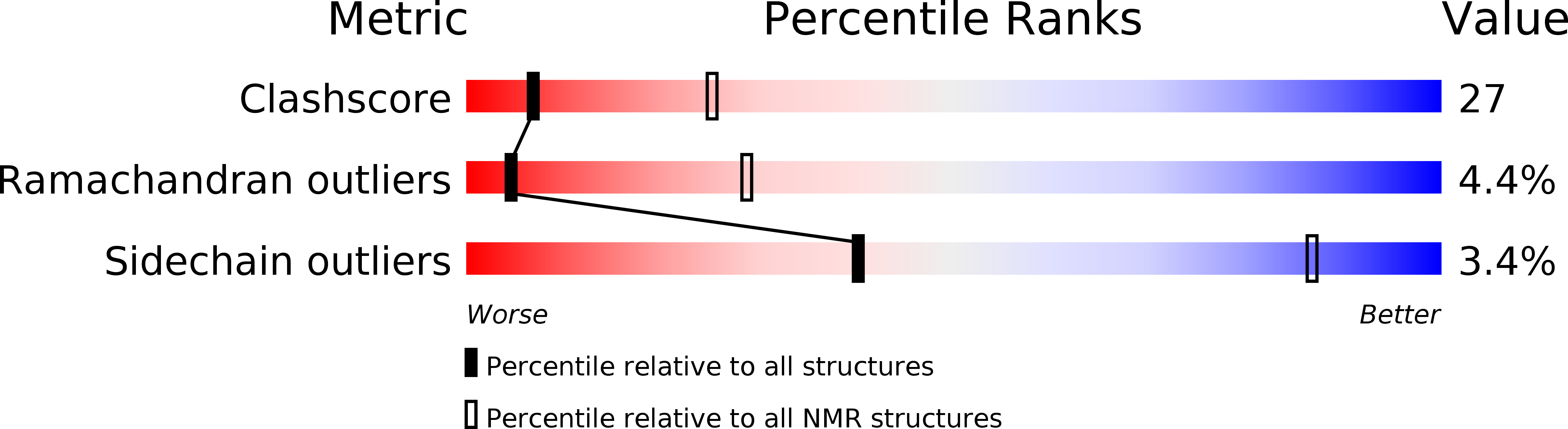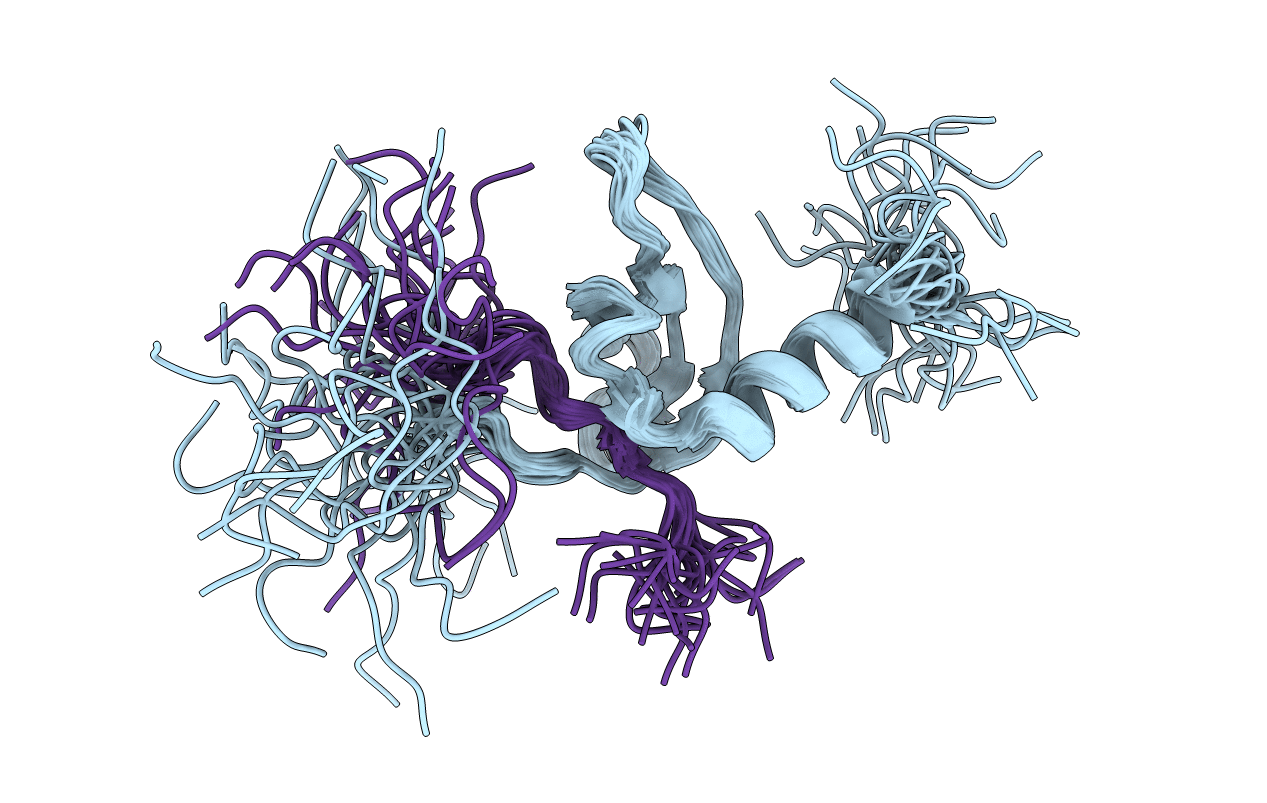
Deposition Date
2002-02-01
Release Date
2002-03-12
Last Version Date
2025-04-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1GUW
Keywords:
Title:
STRUCTURE OF THE CHROMODOMAIN FROM MOUSE HP1beta IN COMPLEX WITH THE LYSINE 9-METHYL HISTONE H3 N-TERMINAL PEPTIDE, NMR, 25 STRUCTURES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
MUS MUSCULUS (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
25
Selection Criteria:
LOWEST ENERGY OF 75 CONVERGED STRUCTURES