Deposition Date
2005-04-20
Release Date
2006-02-14
Last Version Date
2023-08-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1ZFT
Keywords:
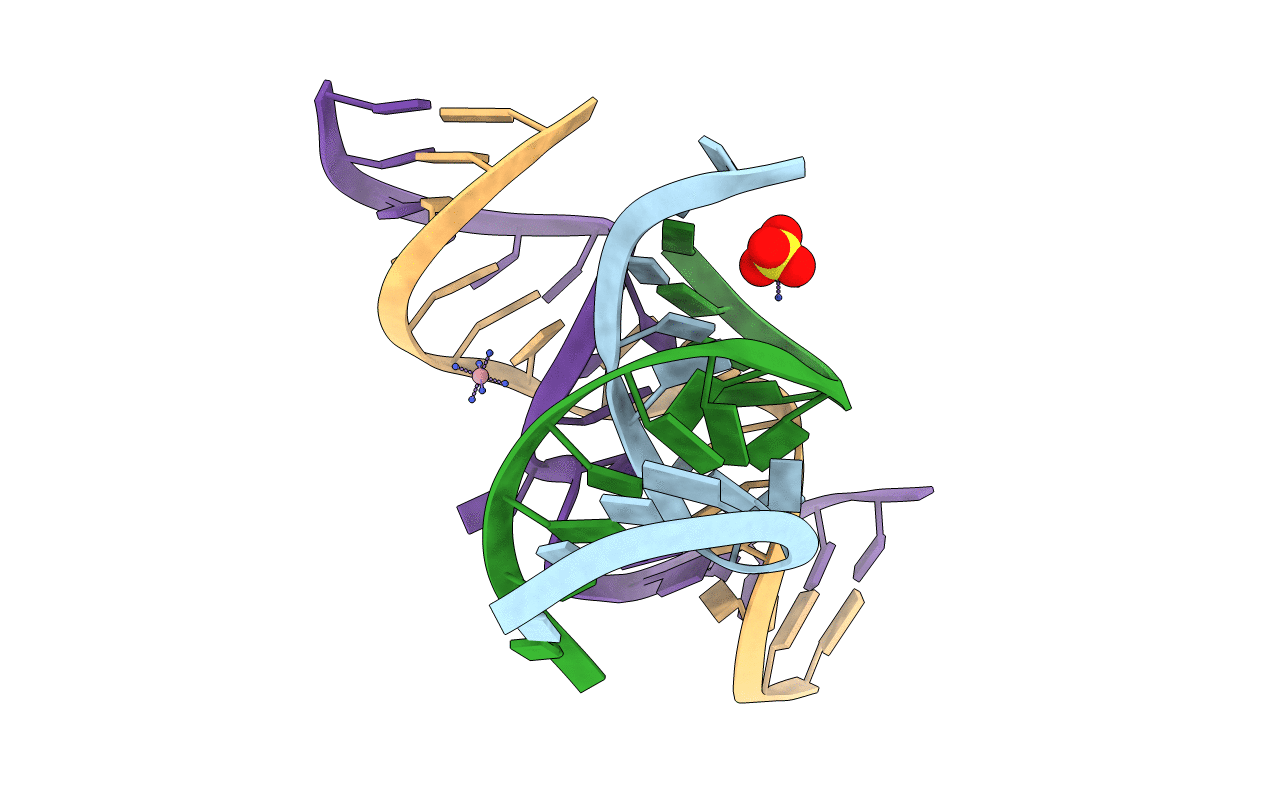
Title:
The crystal structure of an all-RNA minimal Hairpin Ribozyme with mutant G8I at the cleavage site
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
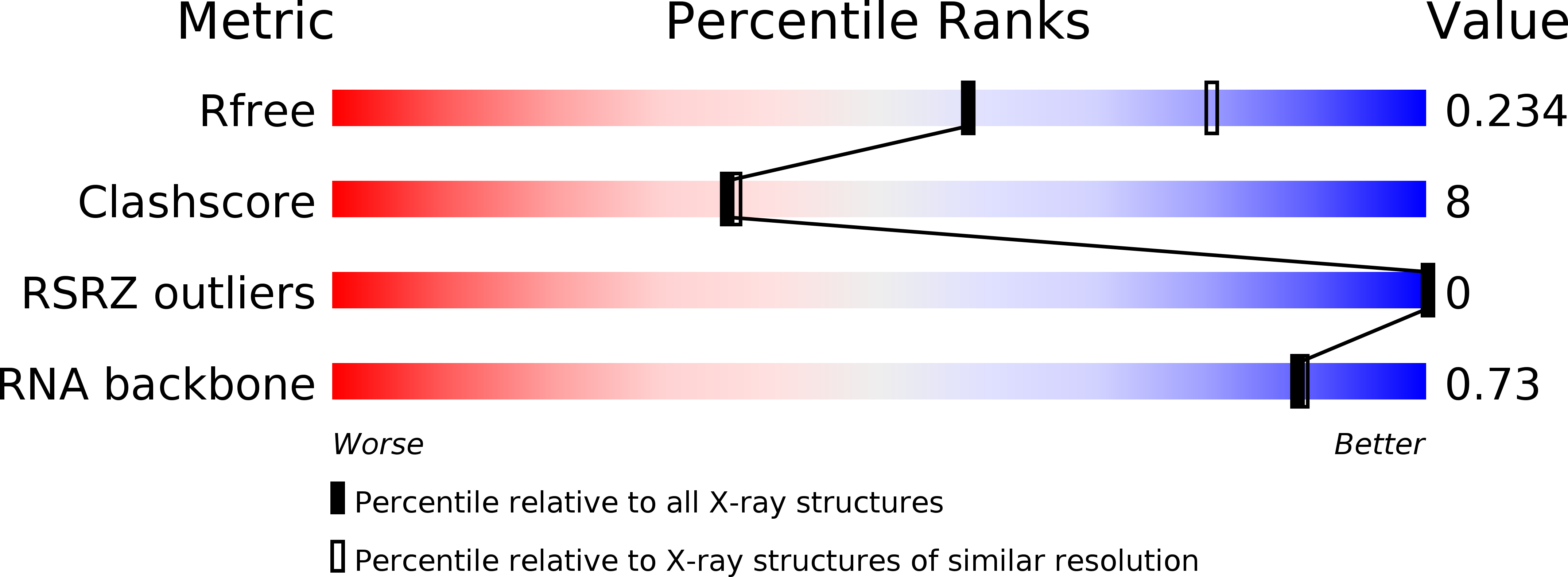
Resolution:
2.33 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 61 2 2