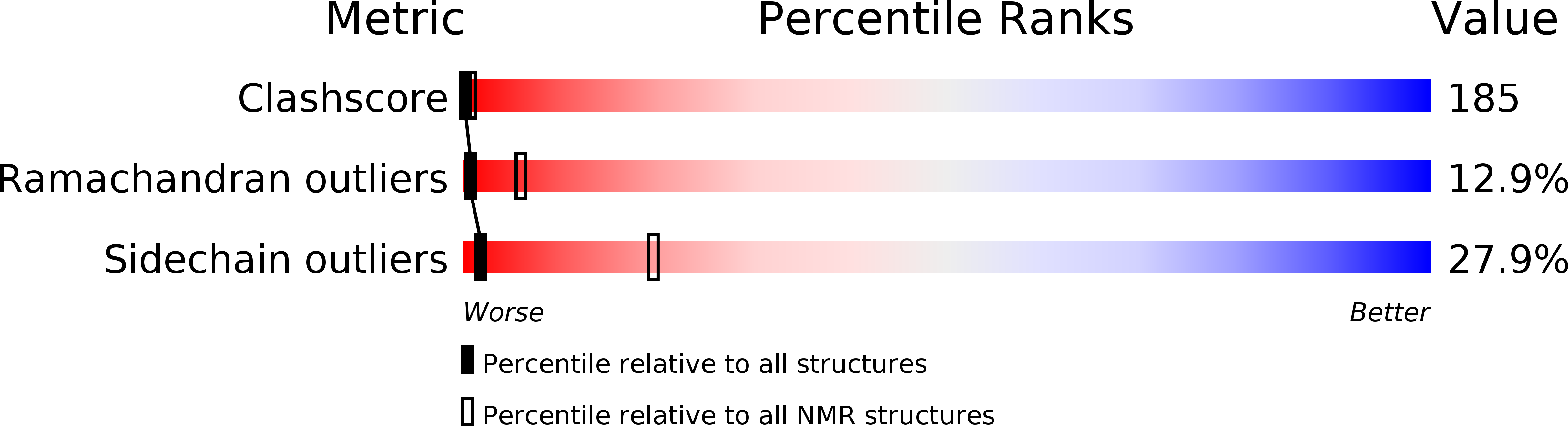
Deposition Date
1996-09-28
Release Date
1997-10-08
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
34
Selection Criteria:
SEE JRNL REFERENCE