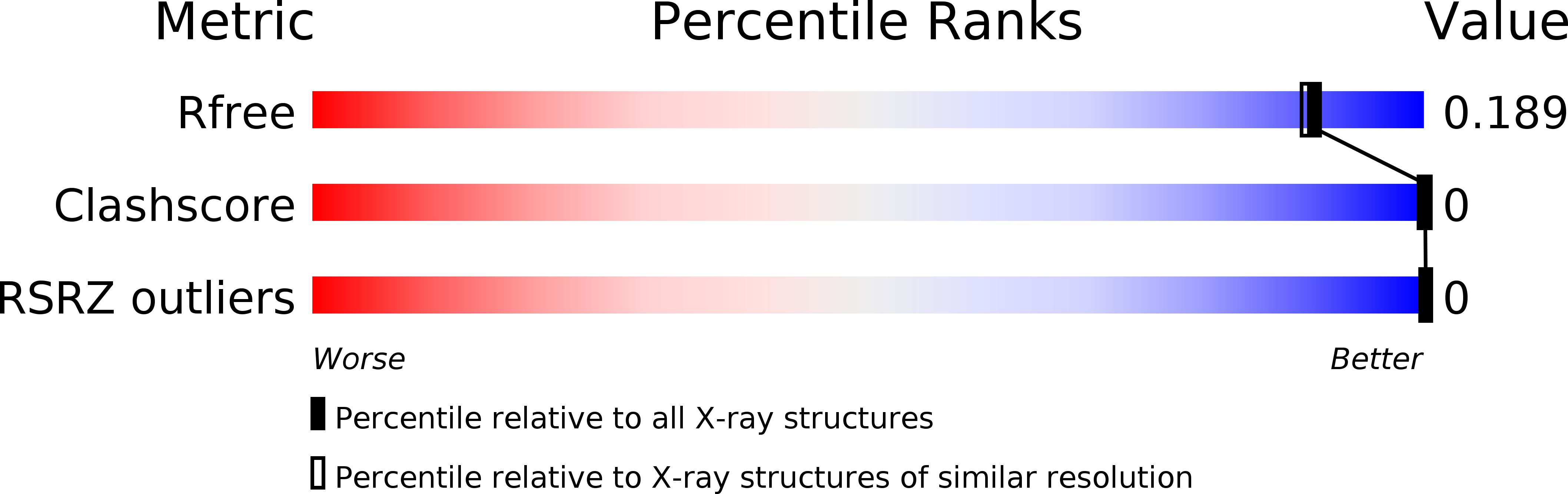Deposition Date
2004-12-10
Release Date
2005-06-28
Last Version Date
2023-08-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1Y86
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the A-DNA GCGTAT*CGC with a 2'-O-[2-(fluoro)ethyl] Thymidine (T*)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21