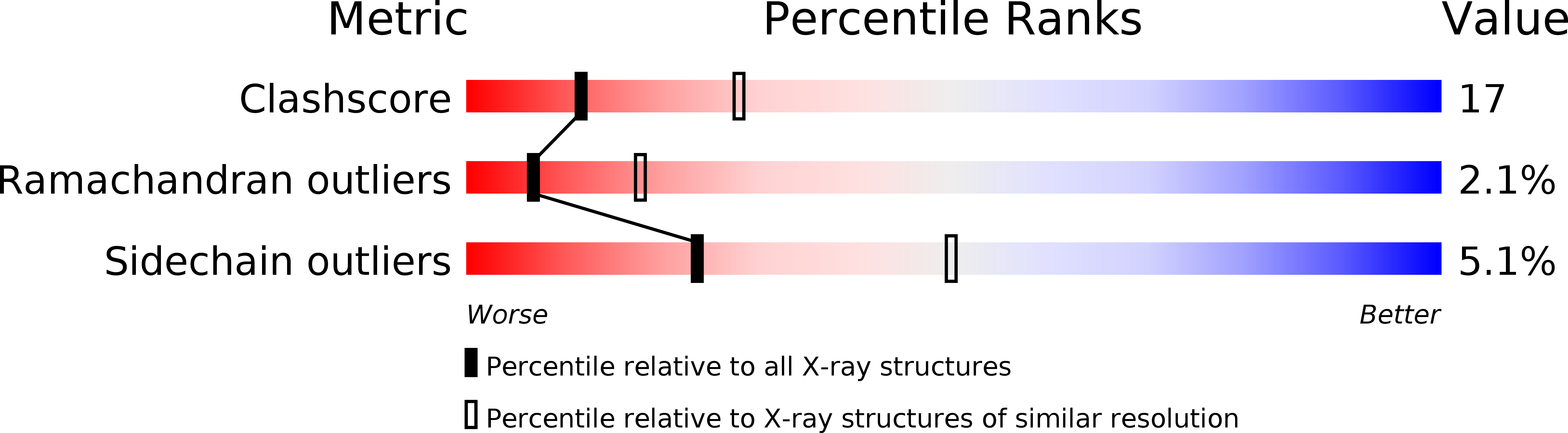Deposition Date
2004-11-09
Release Date
2005-03-15
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1XXW
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of zinc induced heterodimer of two calcium free isoforms of phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera at 2.7A resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Naja sagittifera (Taxon ID: 195058)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 41