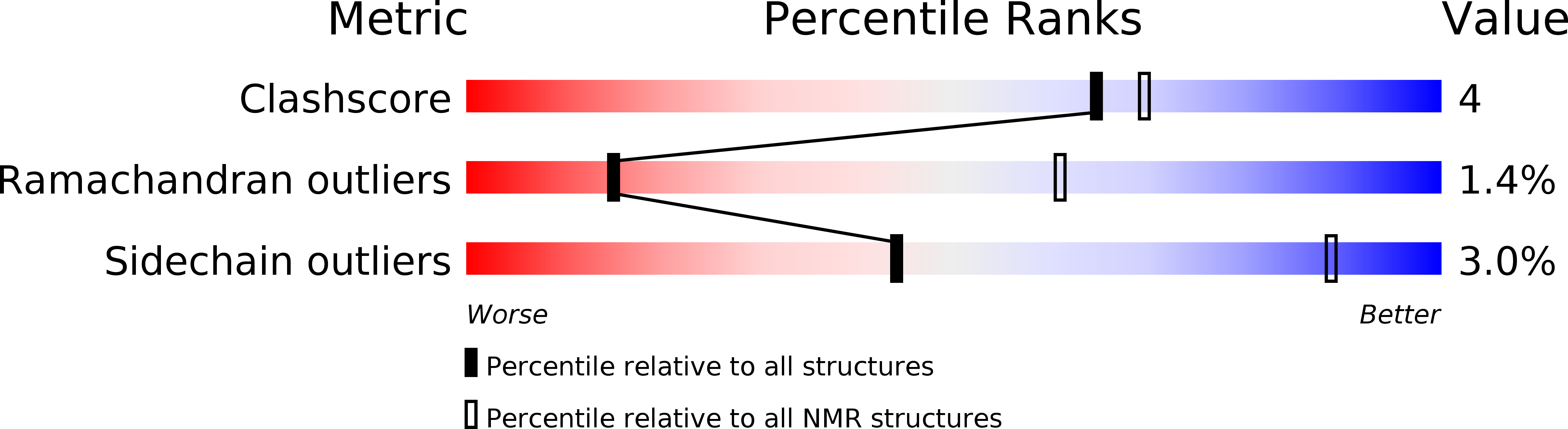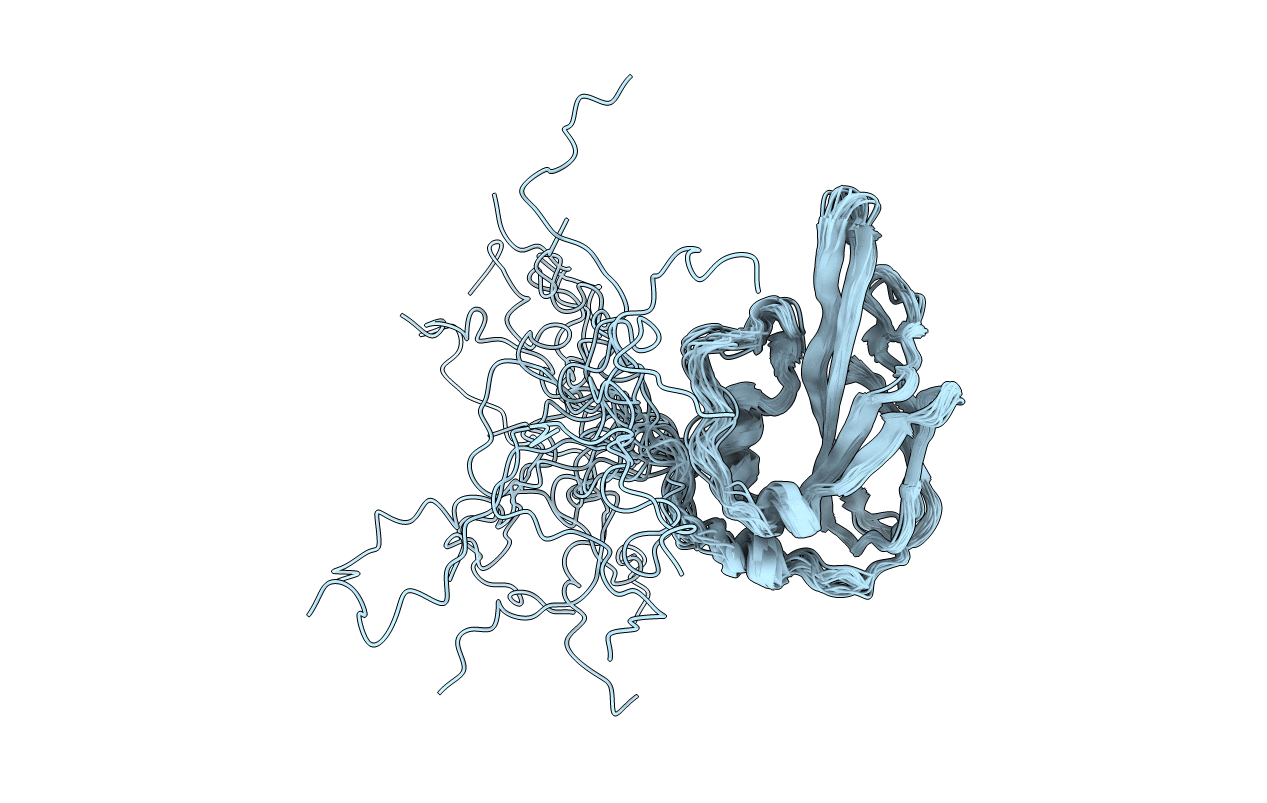
Deposition Date
2004-10-08
Release Date
2004-11-23
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1XPN
Keywords:
Title:
NMR structure of P. aeruginosa protein PA1324: Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium target PaP1
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 208964)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy,structures with the fewest restraint violations