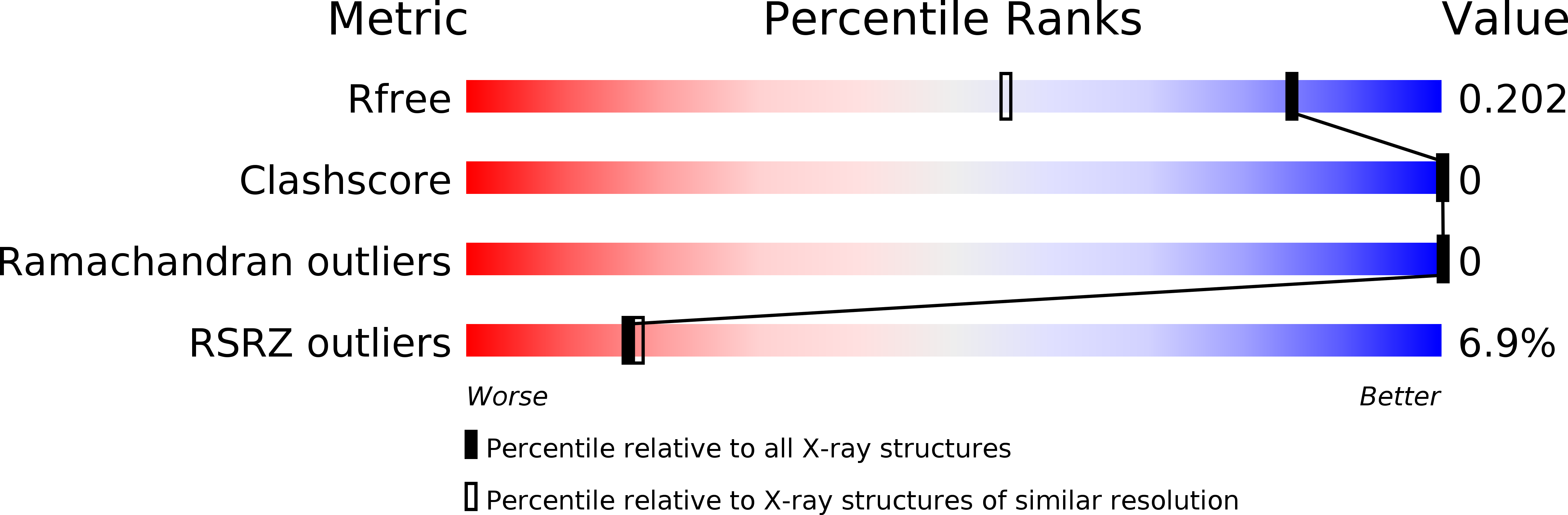Deposition Date
2005-03-03
Release Date
2006-01-31
Last Version Date
2023-10-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1WZB
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the collagen triple helix model [{HYP(R)-HYP(R)-GLY}10]3
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 1 21 1