Abstact
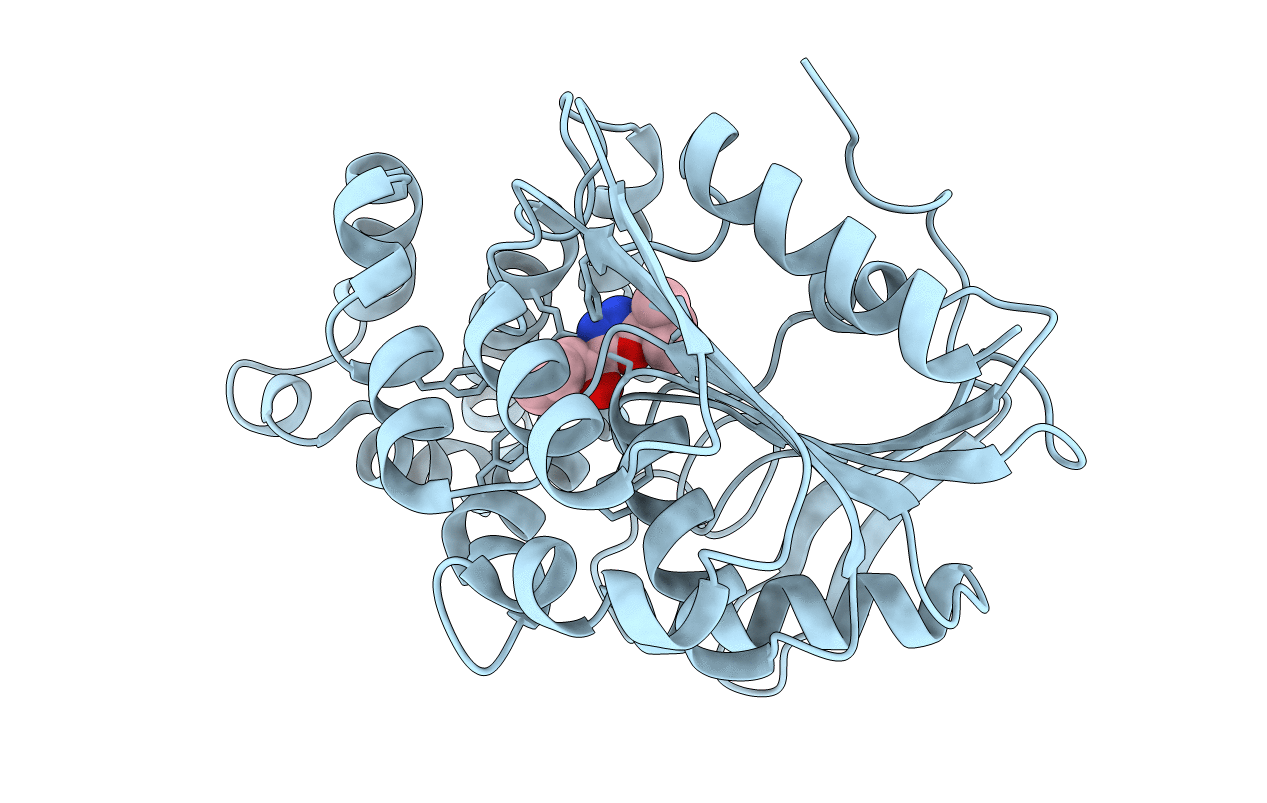
Prolyl aminopeptidase from Serratia marcescens hydrolyzed x-beta-naphthylamides (x=prolyl, alanyl, sarcosinyl, L-alpha-aminobutylyl, and norvalyl), which suggested that the enzyme has a pocket for a five-member ring. Based on the substrate specificity, novel inhibitors of Pro, Ala, and Sar having 2-tert-butyl-[1,3,4]oxadiazole (TBODA) were synthesized. The K(i) value of Pro-TBODA, Ala-TBODA, and Sar-TBODA was 0.5 microM, 1.6 microM, and 12mM, respectively. The crystal structure of enzyme-Pro-TBODA complex was determined. Pro-TBODA was located at the active site. Four electrostatic interactions were located between the enzyme and the amino group of Pro inhibitors (Glu204:0E1-N:Inh, Glu204:0E2-N:Inh, Glu232:0E1-N:Inh, and Gly46:O-N:Inh), and the residue of the inhibitors was inserted into the hydrophobic pocket composed of Phe139, Leu141, Leu146, Tyr149, Tyr150, and Phe236. The roles of Phe139, Tyr149, and Phe236 in the hydrophobic pocket and Glu204 and Glu232 in the electrostatic interactions were confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis, which indicated that the molecular recognition of proline is achieved through four electrostatic interactions and an insertion in the hydrophobic pocket of the enzyme.