Deposition Date
2004-06-02
Release Date
2004-09-07
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1WKR
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of aspartic proteinase from Irpex lacteus
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces argenteolus subsp. toyonakensis (Taxon ID: 285516)
Irpex lacteus (Taxon ID: 5319)
Irpex lacteus (Taxon ID: 5319)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
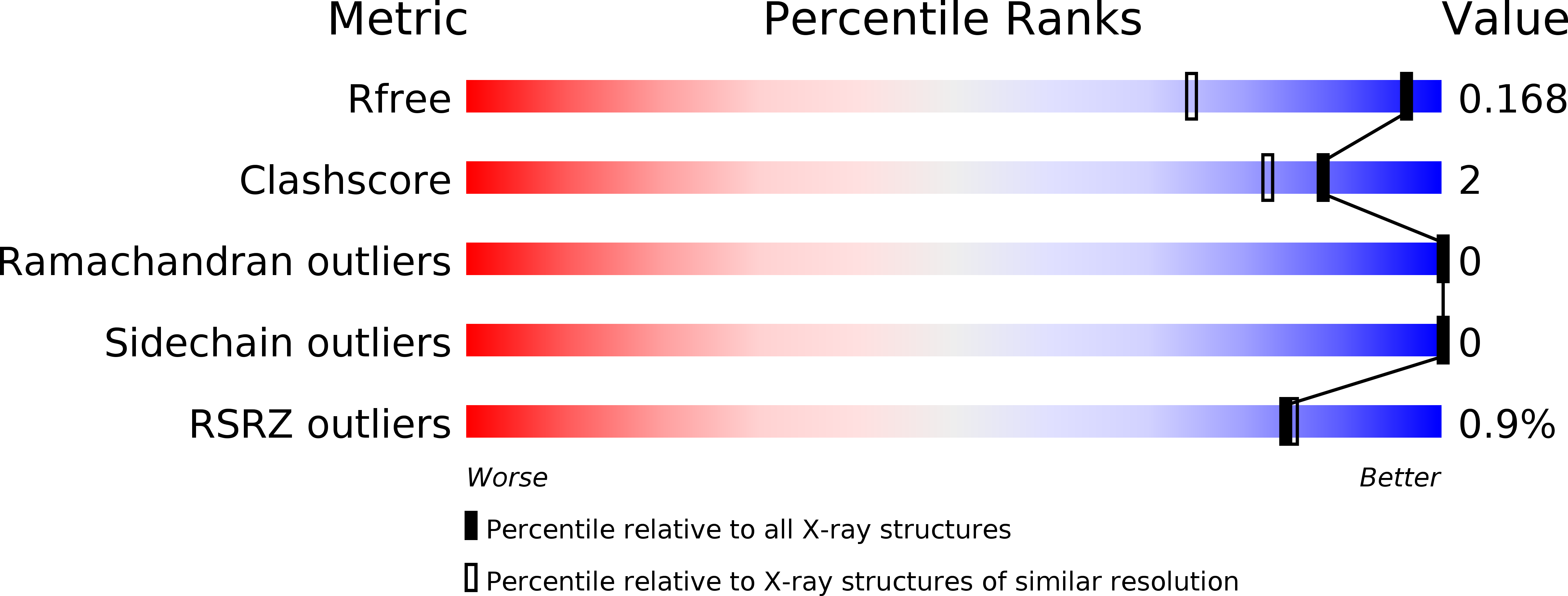
Resolution:
1.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.17
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
P 1 21 1