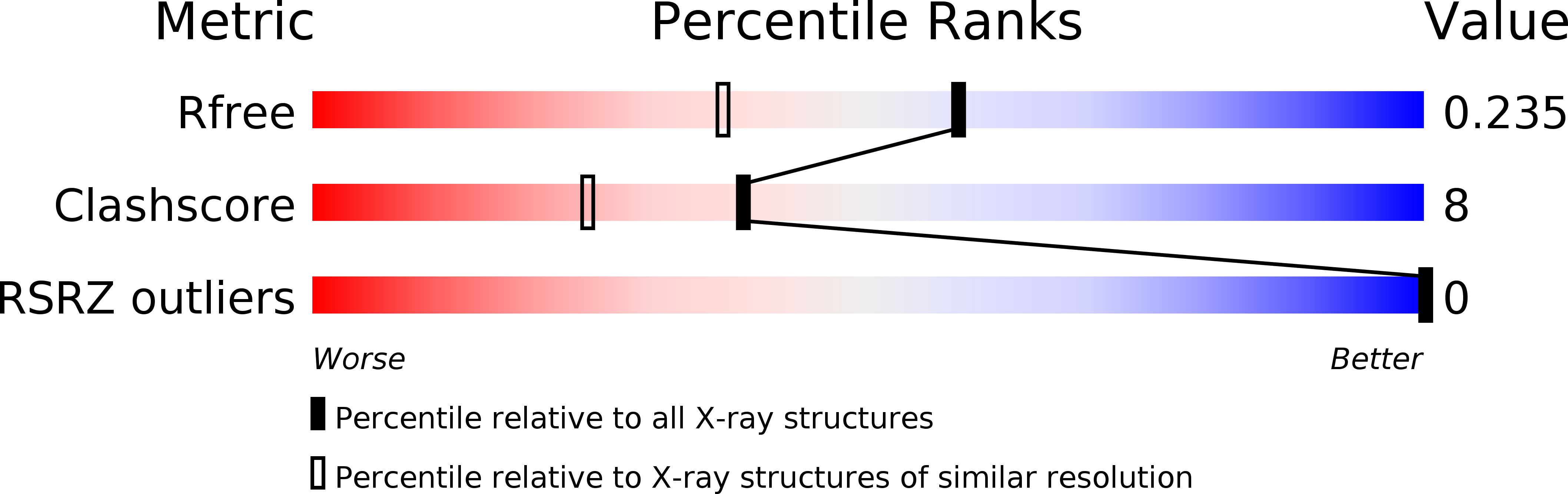Deposition Date
2004-05-20
Release Date
2004-10-25
Last Version Date
2023-12-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1VZK
Keywords:
Title:
A Thiophene Based Diamidine Forms a "Super" AT Binding Minor Groove Agent
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.77 Å
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 21 21 21