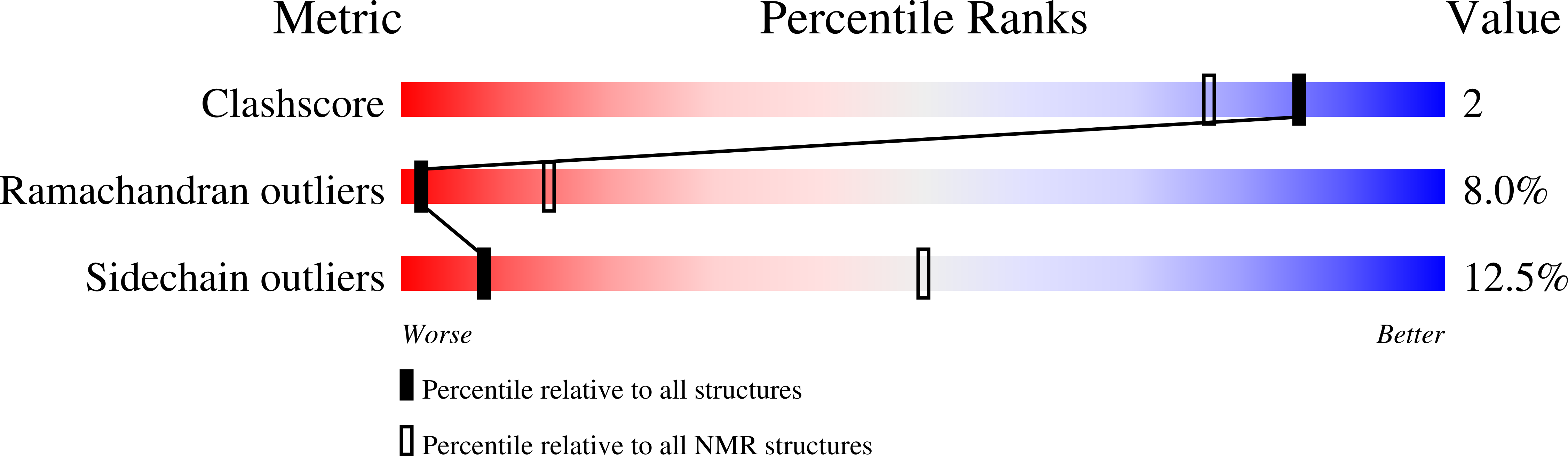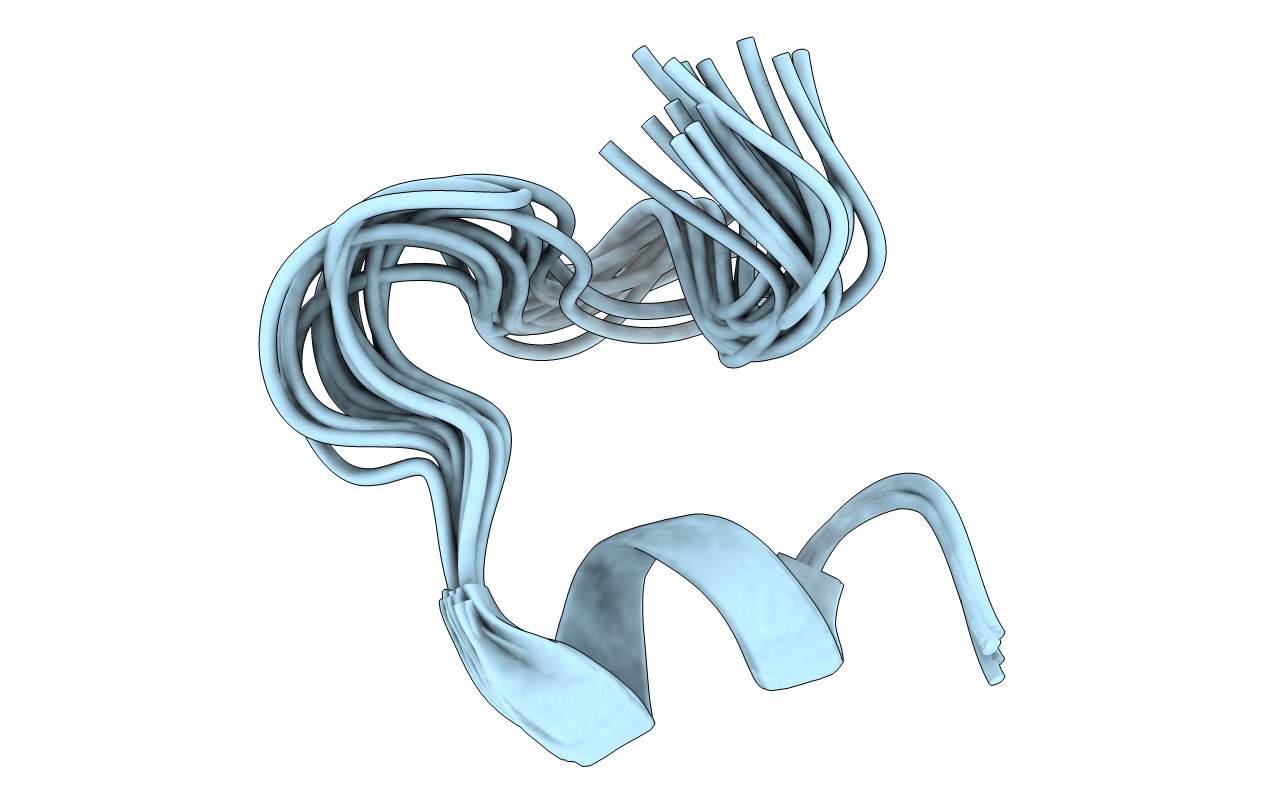
Deposition Date
2005-01-07
Release Date
2005-01-18
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1VQX
Keywords:
Title:
ARRESTIN-BOUND NMR STRUCTURES OF THE PHOSPHORYLATED CARBOXY-TERMINAL DOMAIN OF RHODOPSIN, REFINED
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
15
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy