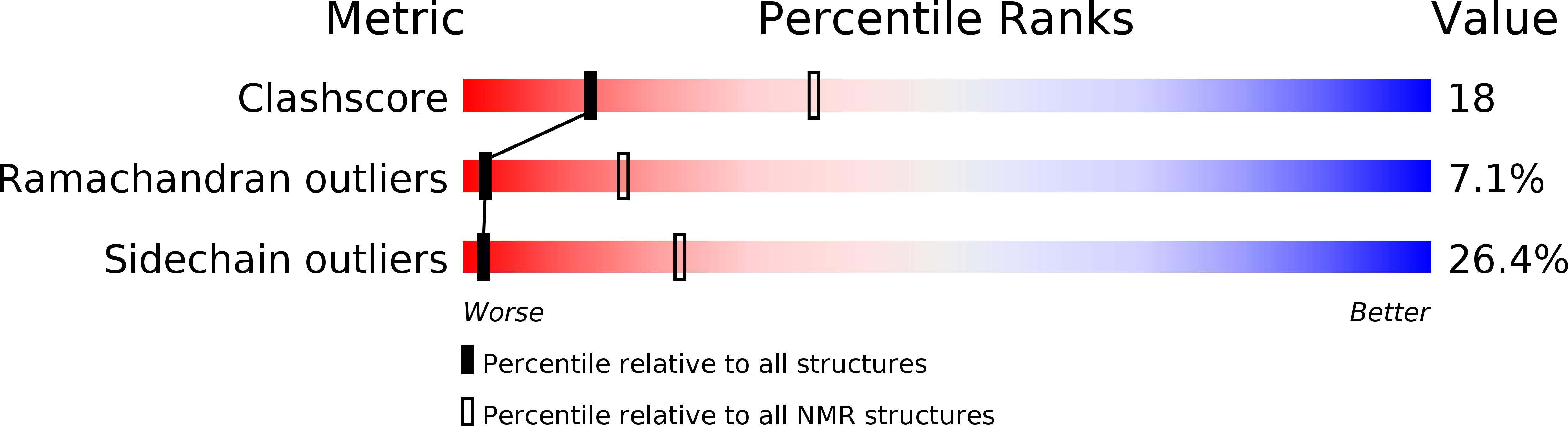
Deposition Date
2004-04-14
Release Date
2005-04-14
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1V1D
Keywords:
Title:
Nucleophilic and General Acid Catalysis at Physiological pH by a Designed Miniature Esterase
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
BOS TAURUS (Taxon ID: 9913)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
NO VIOLATIONS