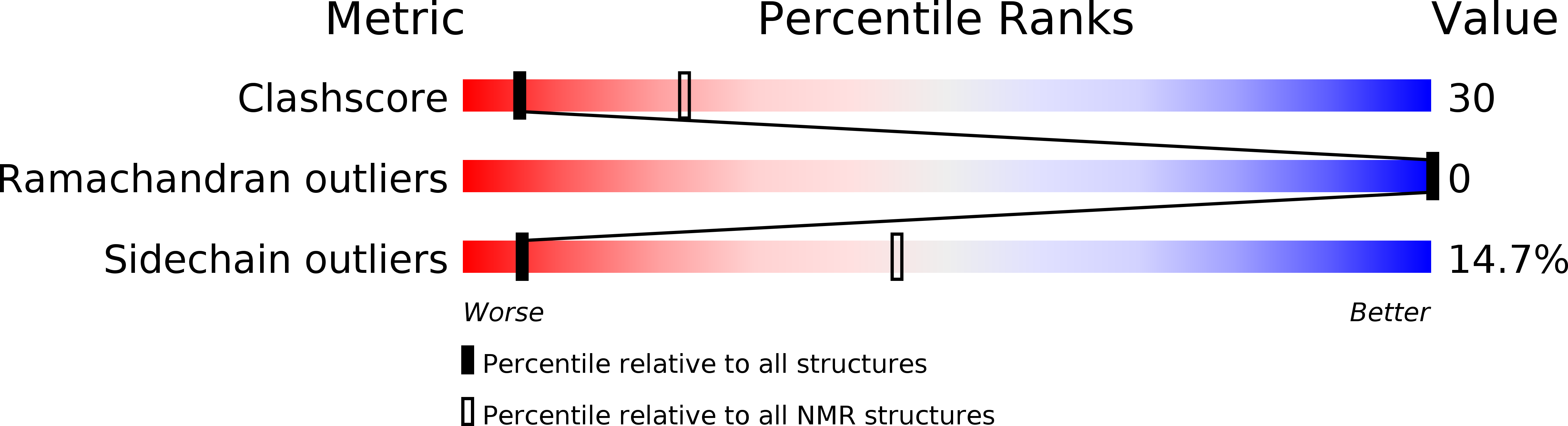
Deposition Date
2003-08-28
Release Date
2003-11-21
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1UMQ
Keywords:
Title:
solution structure and DNA binding of the effector domain from the global regulator PrrA(RegA) from R. sphaeroides: Insights into DNA binding specificity
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
RHODOBACTER SPHAEROIDES (Taxon ID: 1063)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
5
Selection Criteria:
RANDOM