Deposition Date
2004-08-07
Release Date
2004-12-21
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
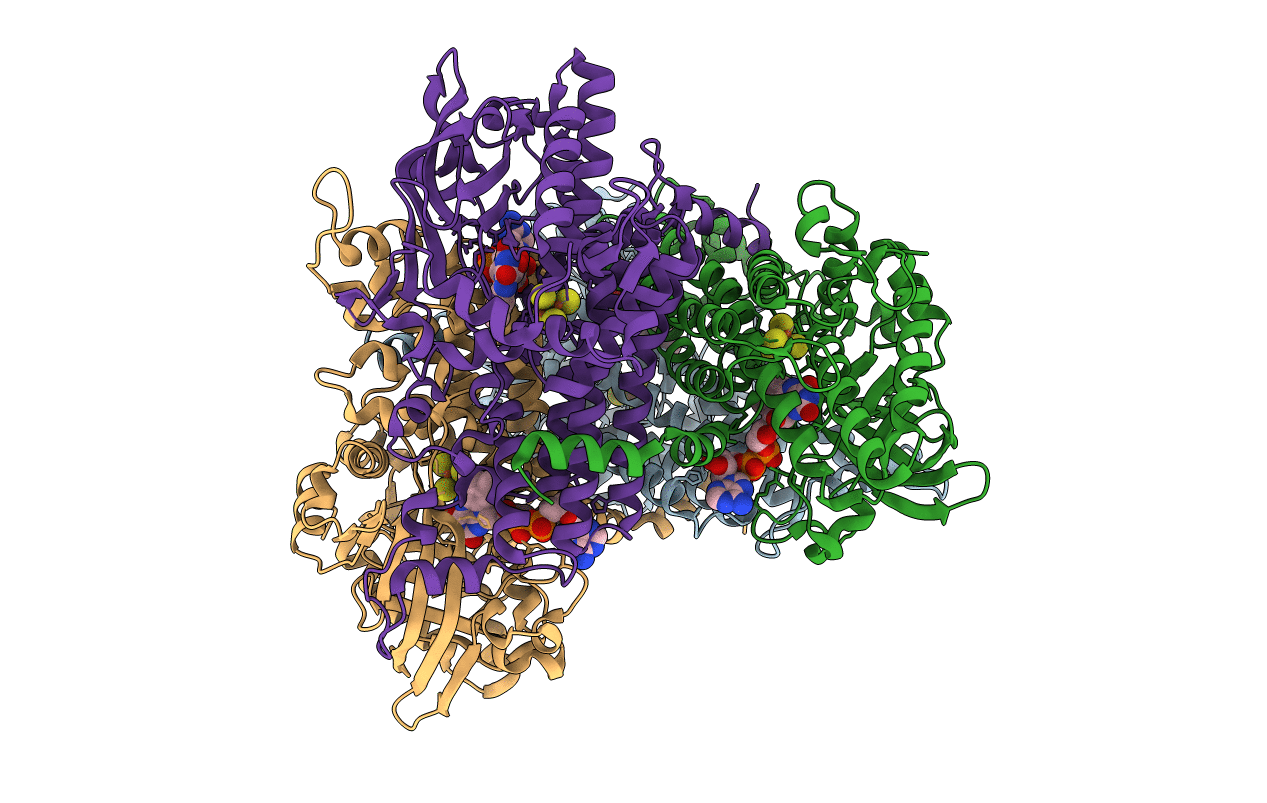
PDB ID:
1U8V
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of 4-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA Dehydratase from Clostridium aminobutyricum: Radical catalysis involving a [4Fe-4S] cluster and flavin
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Clostridium aminobutyricum (Taxon ID: 33953)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.60 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 21 21 21


