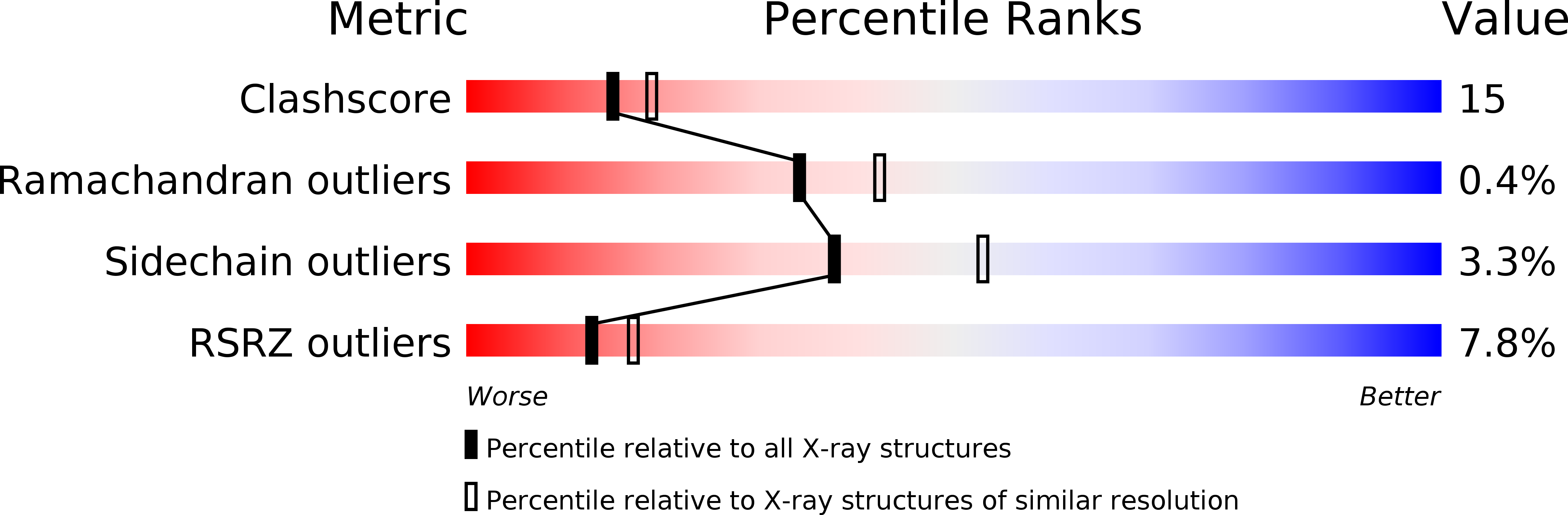Abstact
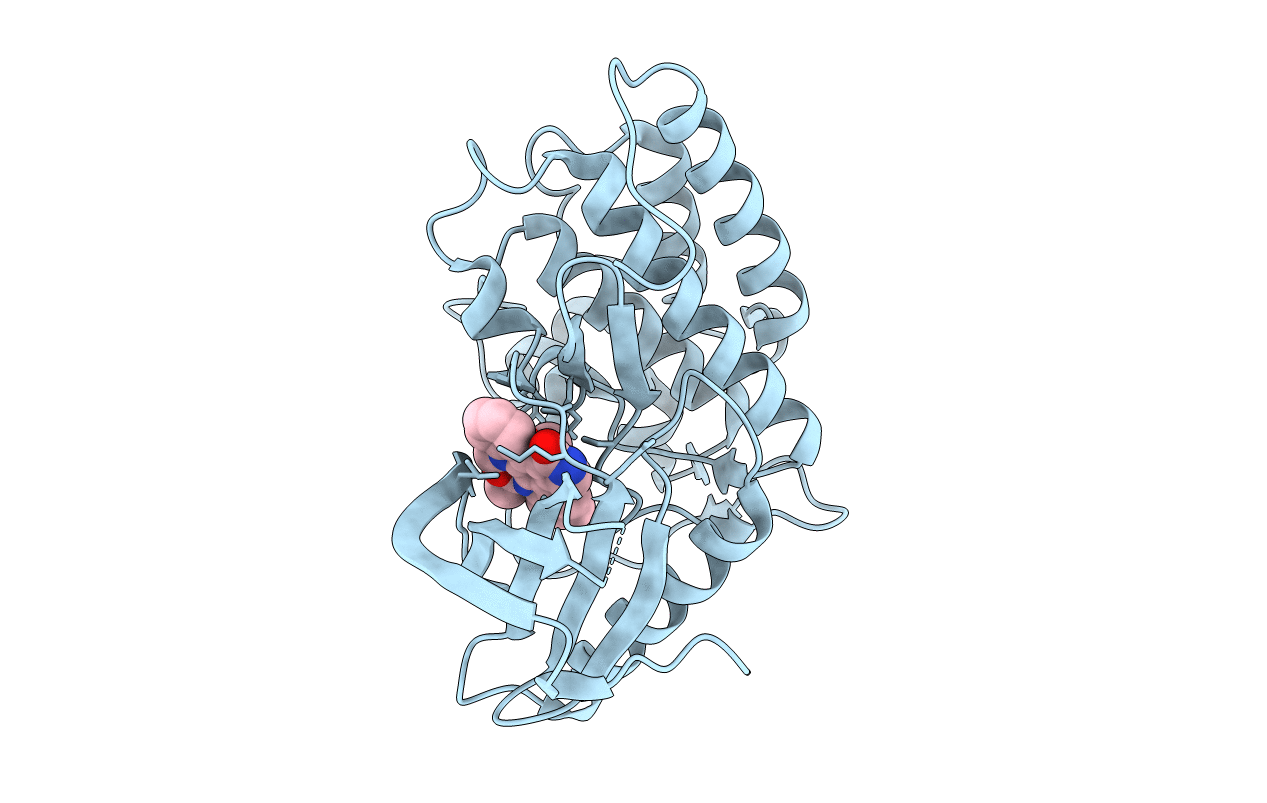
The ZAP-70 tyrosine kinase plays a critical role in T cell activation and the immune response and therefore is a logical target for immunomodulatory therapies. Although the crystal structure of the tandem Src homology-2 domains of human ZAP-70 in complex with a peptide derived from the zeta subunit of the T cell receptor has been reported (Hatada, M. H., Lu, X., Laird, E. R., Green, J., Morgenstern, J. P., Lou, M., Marr, C. S., Phillips, T. B., Ram, M. K., Theriault, K., Zoller, M. J., and Karas, J. L. (1995) Nature 377, 32-38), the structure of the kinase domain has been elusive to date. We crystallized and determined the three-dimensional structure of the catalytic subunit of ZAP-70 as a complex with staurosporine to 2.3 A resolution, utilizing an active kinase domain containing residues 327-606 identified by systematic N- and C-terminal truncations. The crystal structure shows that this ZAP-70 kinase domain is in an active-like conformation despite the lack of tyrosine phosphorylation in the activation loop. The unique features of the ATP-binding site, identified by structural and sequence comparison with other kinases, will be useful in the design of ZAP-70-selective inhibitors.