Deposition Date
2004-07-16
Release Date
2004-12-07
Last Version Date
2023-08-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1U1Y
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of a complex between WT bacteriophage MS2 coat protein and an F5 aptamer RNA stemloop with 2aminopurine substituted at the-10 position
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Enterobacterio phage MS2 (Taxon ID: 12022)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
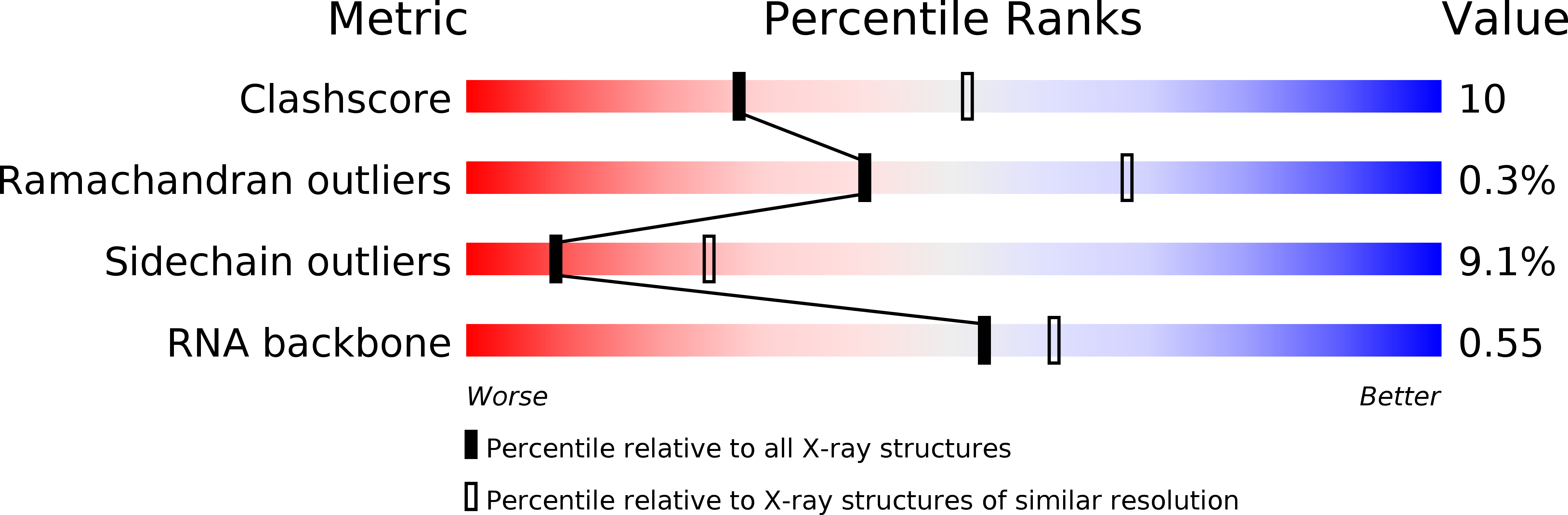
Resolution:
2.85 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
H 3 2