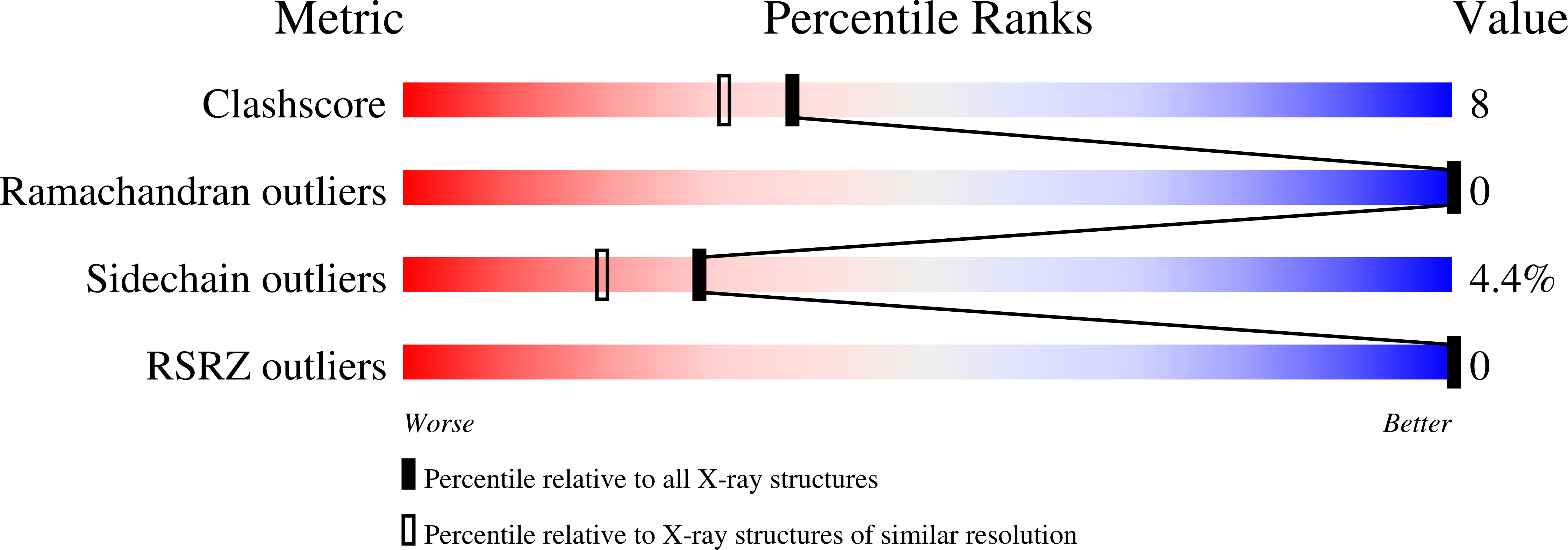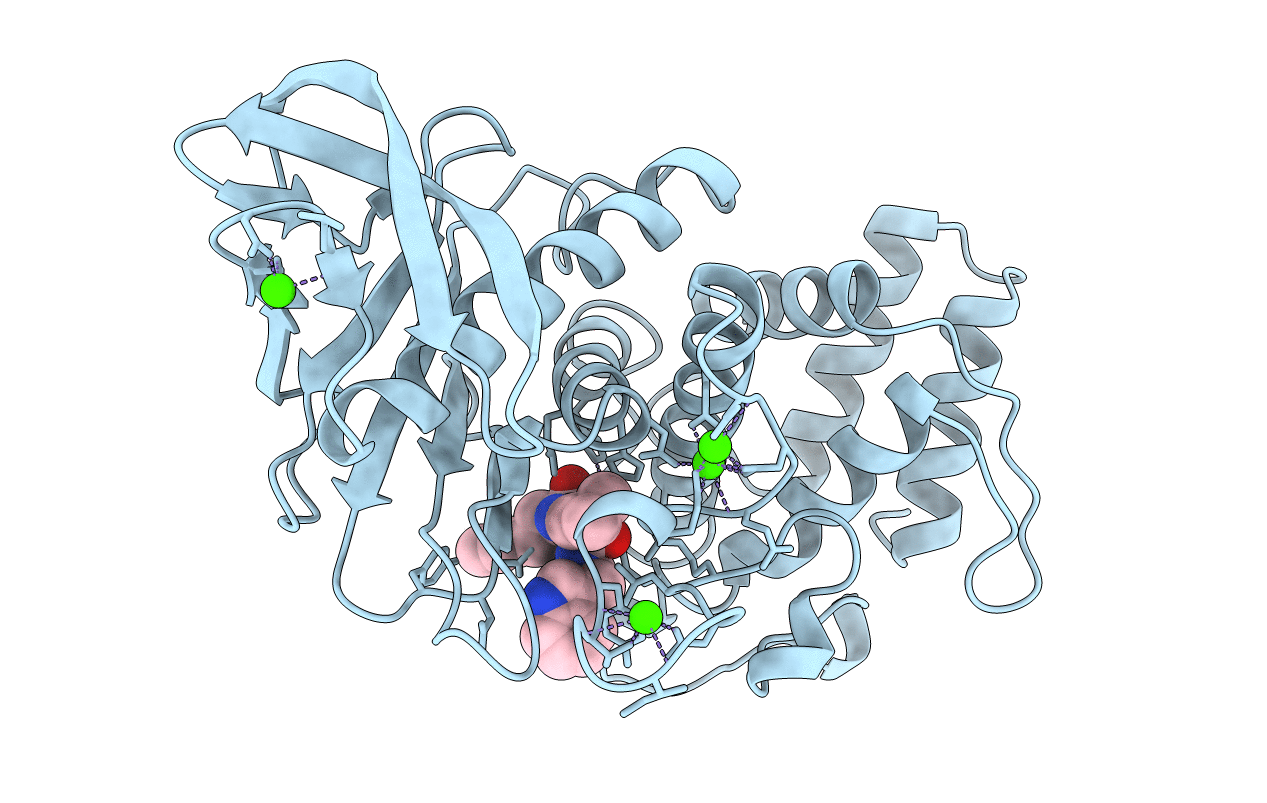
Deposition Date
1987-06-29
Release Date
1989-01-09
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1TMN
Keywords:
Title:
Binding of n-carboxymethyl dipeptide inhibitors to thermolysin determined by x-ray crystallography. a novel class of transition-state analogues for zinc peptidases
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bacillus thermoproteolyticus (Taxon ID: 1427)
Method Details: