Deposition Date
2004-06-02
Release Date
2004-06-15
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1TID
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structures of the ADP and ATP bound forms of the Bacillus Anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB in complex with the Anti-anti-sigma SpoIIAA: Poised for phosphorylation complex with ATP, crystal form I
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Taxon ID: 1422)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
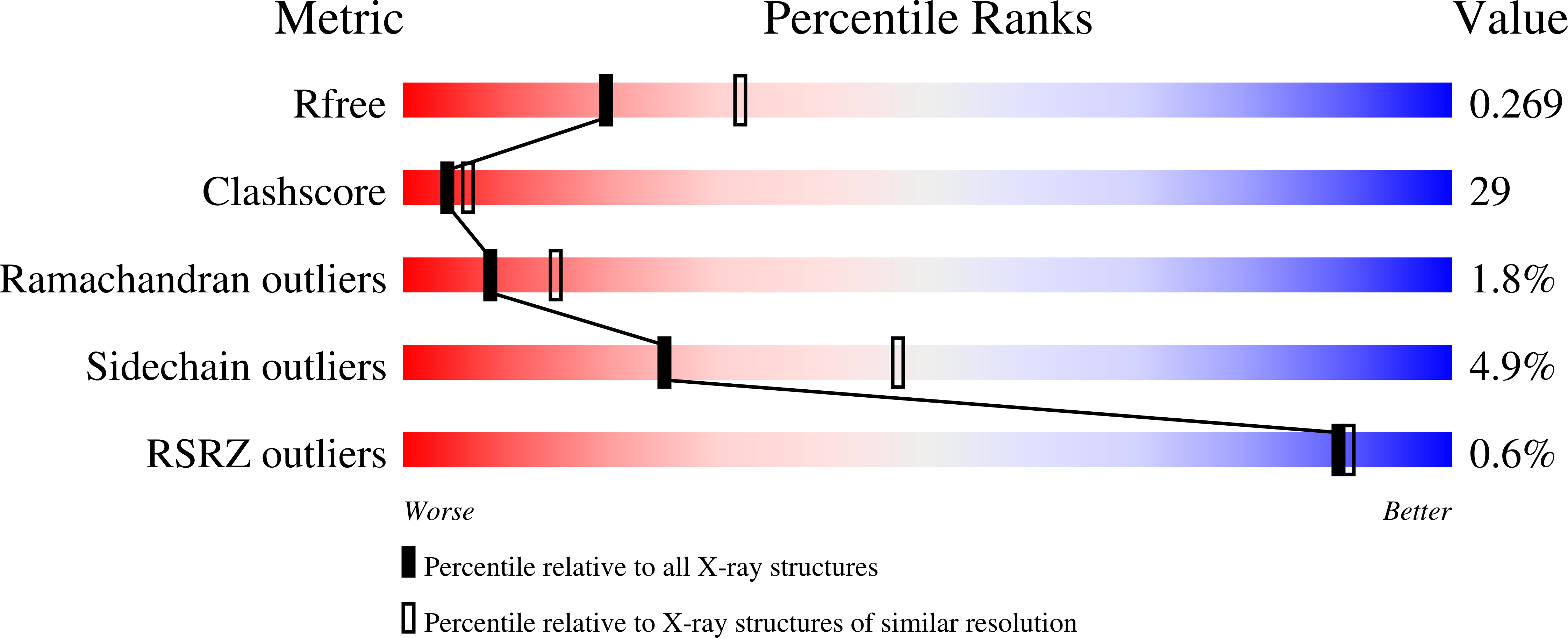
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.23
Space Group:
P 41