Abstact
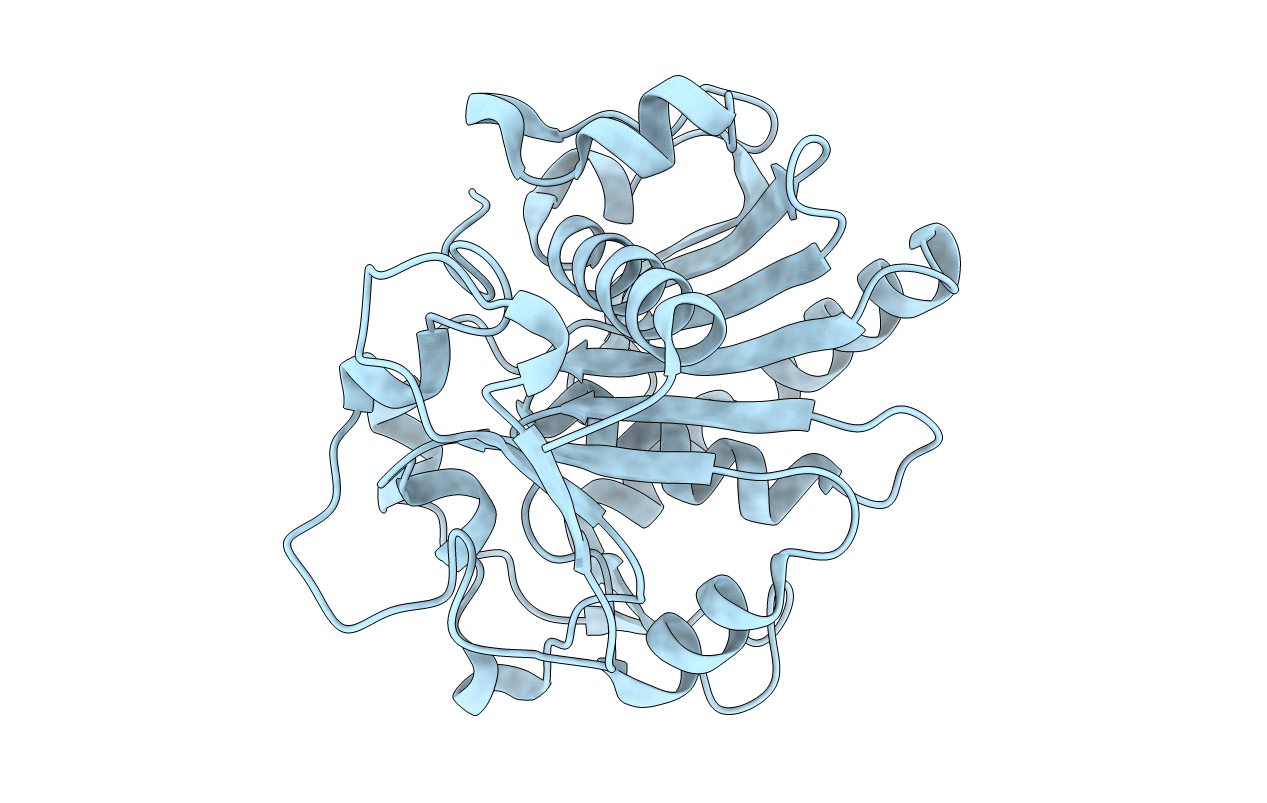
Considerable controversy exists regarding the exact nature of the molecular mechanism of interfacial activation, a process by which most lipases achieve maximum catalytic activity upon adsorption to an oil water interface. X-ray crystallographic studies show that lipases contain buried active centers and that displacements of entire secondary structure elements, or "lids," take place when the enzymes assume active conformations [Derewenda, U., A. M. Brzozowski, D. M. Lawson, and Z. S. Derewenda. 1992. Biochemistry: 31: 1532-1541; van Tilbeurgh, H., M-P. Egloff, C. Martinez, N. Rugani, R. Verger, and C. Cambillau. 1993. Nature: 362: 814-820; Grochulski, P., L. Yunge, J. D. Schrag, F. Bouthillier, P. Smith, D. Harrison, B. Rubin, and M. Cygler. 1993. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 12843-12847]. A simple two-state model inferred from these results implies that the "closed" conformation is stable in an aqueous medium, rendering the active centers inaccessible to water soluble substrates. We now report that in crystals of the Humicola lanuginosa lipase the "lid" is significantly disordered irrespective of the ionic strength of the medium, while in a related enzyme from Rhizopus delemar, crystallized in the presence of a detergent, the two molecules that form the asymmetric unit show different "lid" conformations. These new results call into question the simplicity of the "enzyme theory" of interfacial activation.