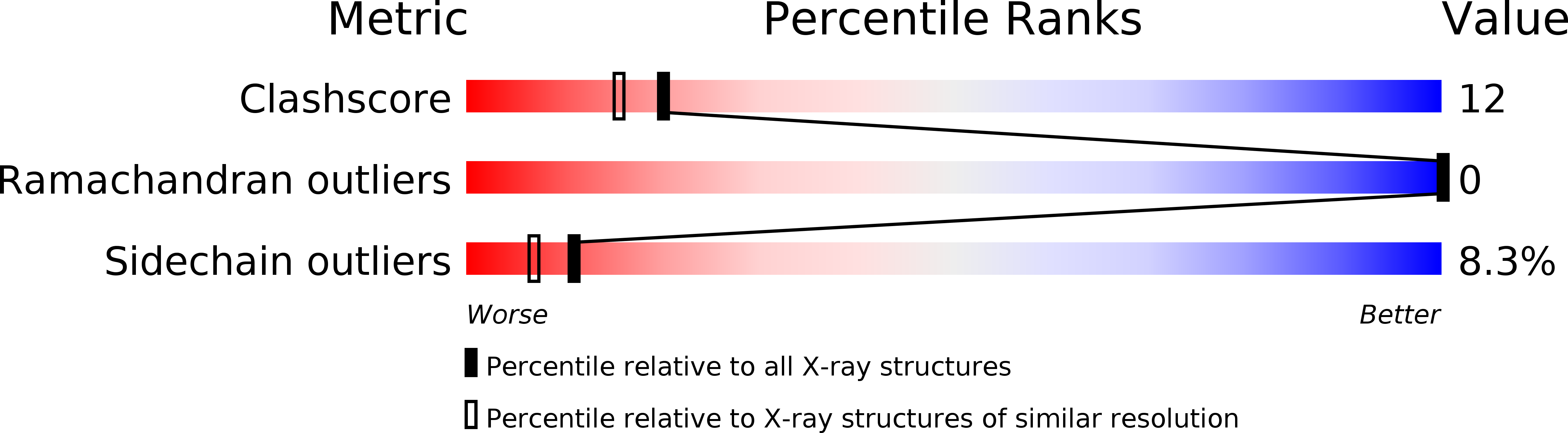
Deposition Date
1994-10-05
Release Date
1995-01-26
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1SSC
Keywords:
Title:
THE 1.6 ANGSTROMS STRUCTURE OF A SEMISYNTHETIC RIBONUCLEASE CRYSTALLIZED FROM AQUEOUS ETHANOL. COMPARISON WITH CRYSTALS FROM SALT SOLUTIONS AND WITH RNASE A FROM AQUEOUS ALCOHOL SOLUTIONS
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 1 21 1