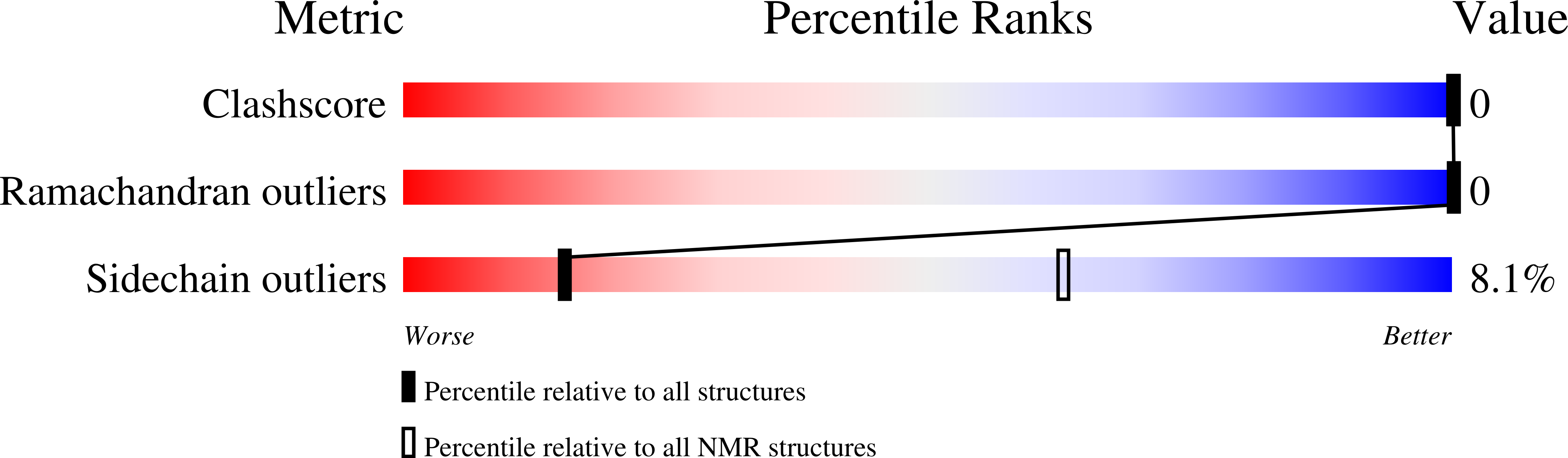
Deposition Date
1994-09-26
Release Date
1994-12-20
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1SPF
Keywords:
Title:
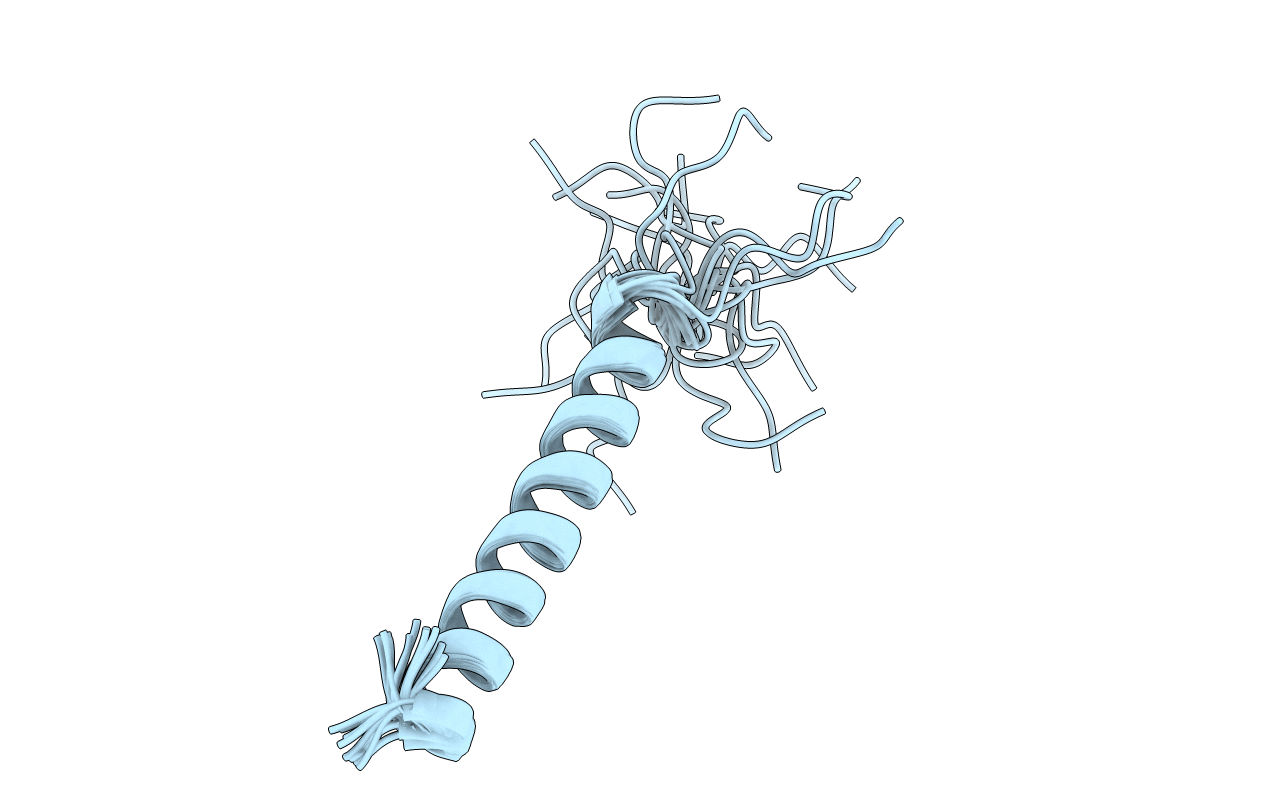
THE NMR STRUCTURE OF THE PULMONARY SURFACTANT-ASSOCIATED POLYPEPTIDE SP-C IN AN APOLAR SOLVENT CONTAINS A VALYL-RICH ALPHA-HELIX
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
20