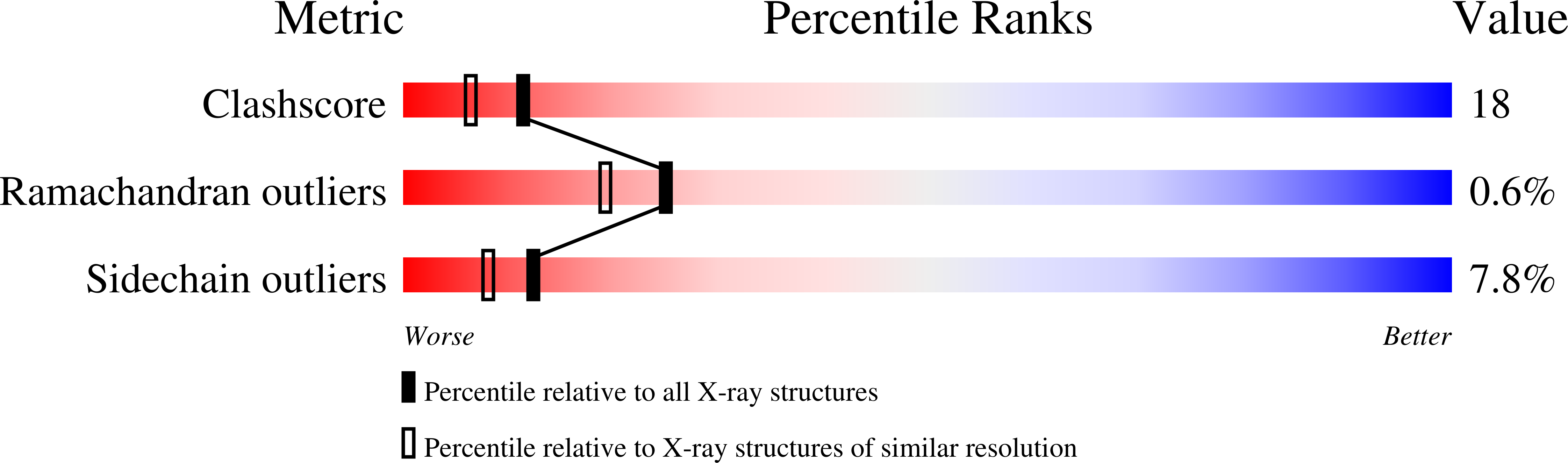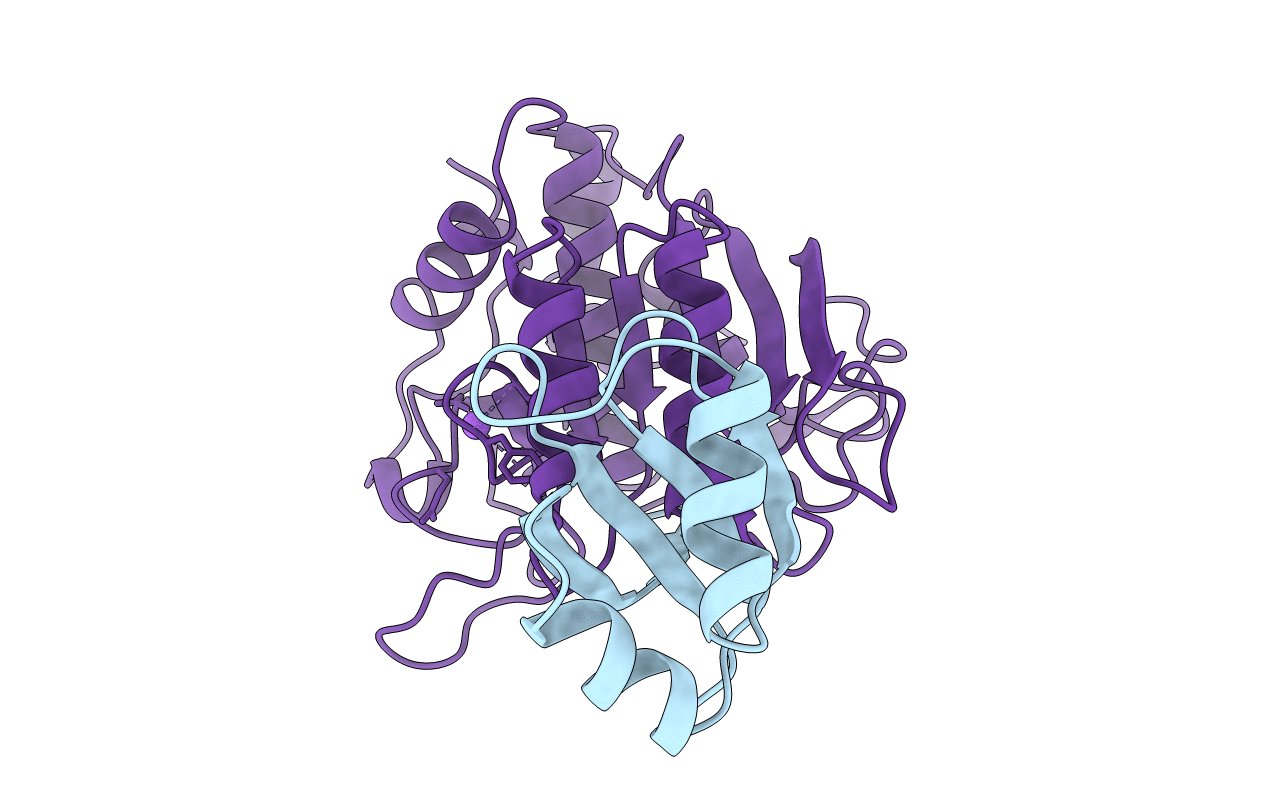
Deposition Date
1995-06-21
Release Date
1995-10-15
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1SPB
Keywords:
Title:
SUBTILISIN BPN' PROSEGMENT (77 RESIDUES) COMPLEXED WITH A MUTANT SUBTILISIN BPN' (266 RESIDUES). CRYSTAL PH 4.6. CRYSTALLIZATION TEMPERATURE 20 C DIFFRACTION TEMPERATURE-160 C
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Taxon ID: 1390)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 21 21 2