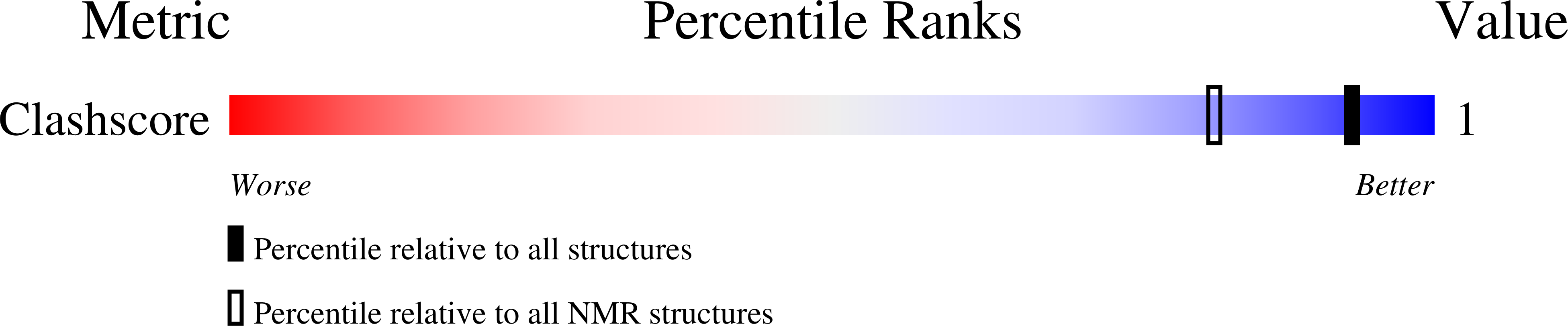
Deposition Date
2004-02-05
Release Date
2005-11-01
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1S9O
Keywords:
Title:
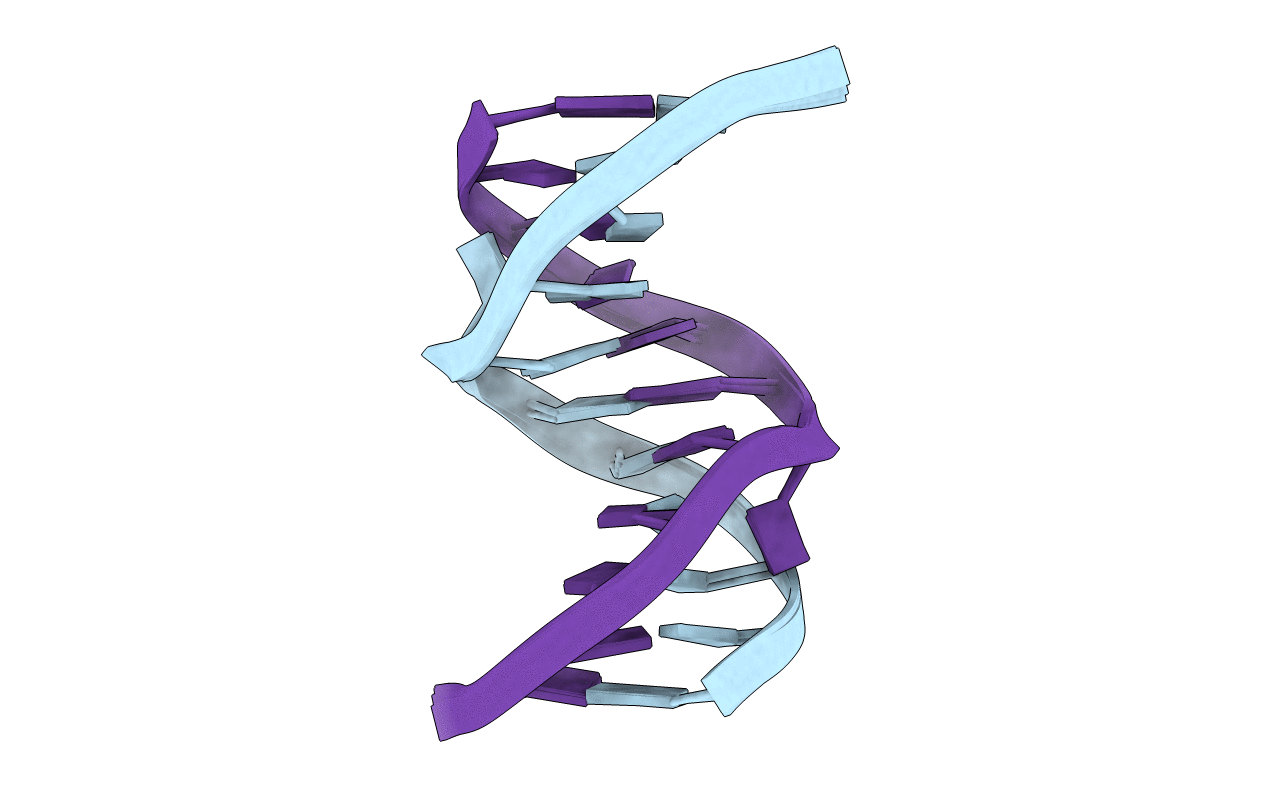
Solution structure of the nitrous acid induced DNA interstrand cross-linked dodecamer duplex CGCTAC(G)TAGCG with the cross-linked guanines denoted (G)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
12
Selection Criteria:
back calculated data agree with experimental NOESY spectrum