Deposition Date
2004-01-08
Release Date
2004-04-13
Last Version Date
2024-04-03
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1S26
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of Anthrax Edema Factor-Calmodulin-alpha,beta-methyleneadenosine 5'-triphosphate Complex Reveals an Alternative Mode of ATP Binding to the Catalytic Site
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bacillus anthracis (Taxon ID: 1392)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
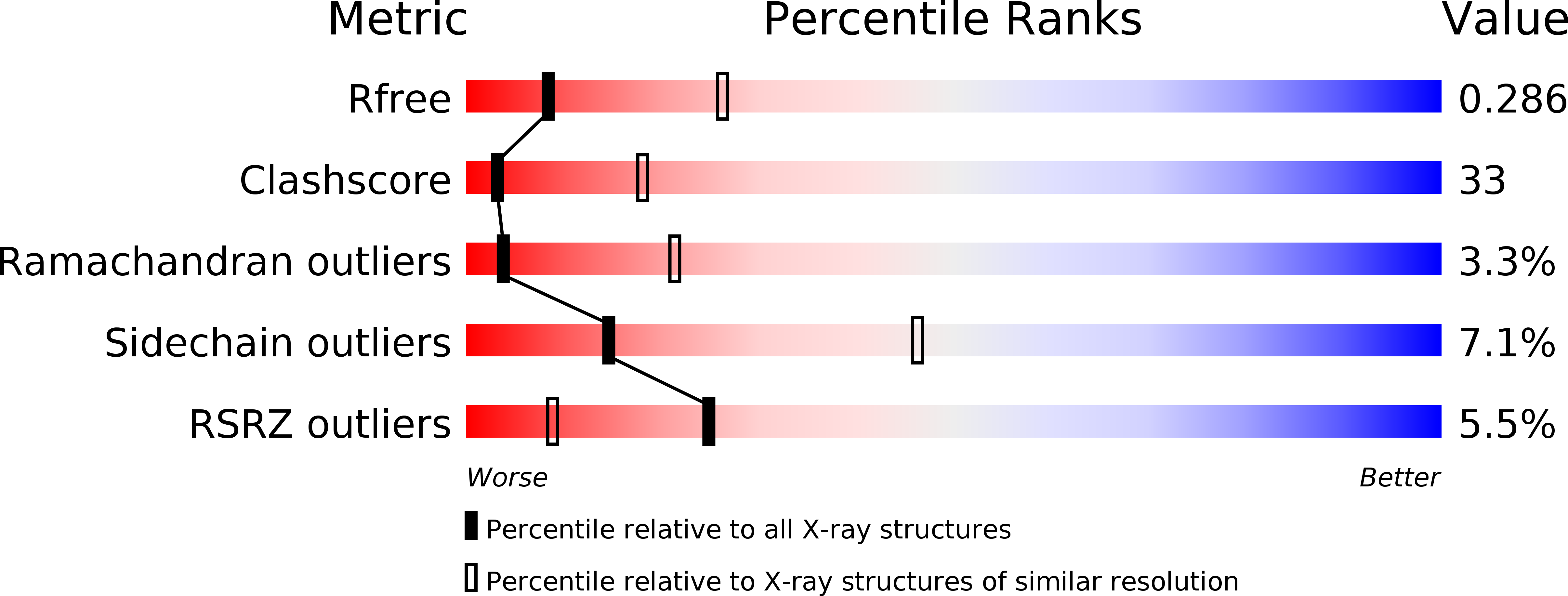
Resolution:
3.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.30
R-Value Work:
0.26
R-Value Observed:
0.26
Space Group:
I 2 2 2