Deposition Date
1994-03-29
Release Date
1995-05-08
Last Version Date
2024-12-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1RSC
Keywords:
Title:
STRUCTURE OF AN EFFECTOR INDUCED INACTIVATED STATE OF RIBULOSE BISPHOSPHATE CARBOXYLASE(SLASH)OXYGENASE: THE BINARY COMPLEX BETWEEN ENZYME AND XYLULOSE BISPHOSPHATE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Synechococcus elongatus (Taxon ID: 269084)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
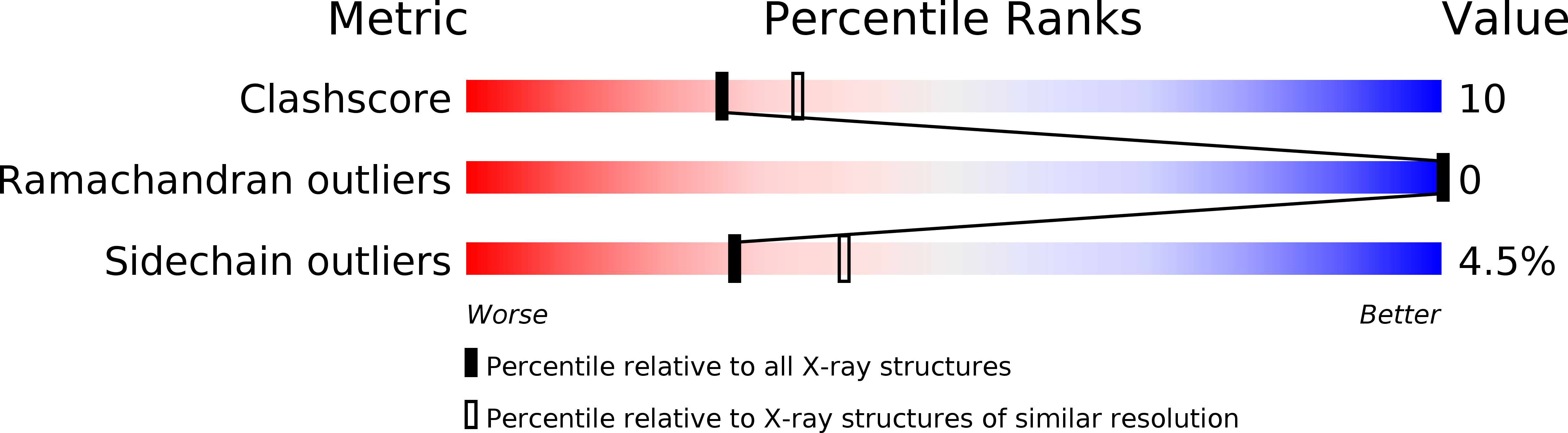
Resolution:
2.30 Å
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 21 21 21