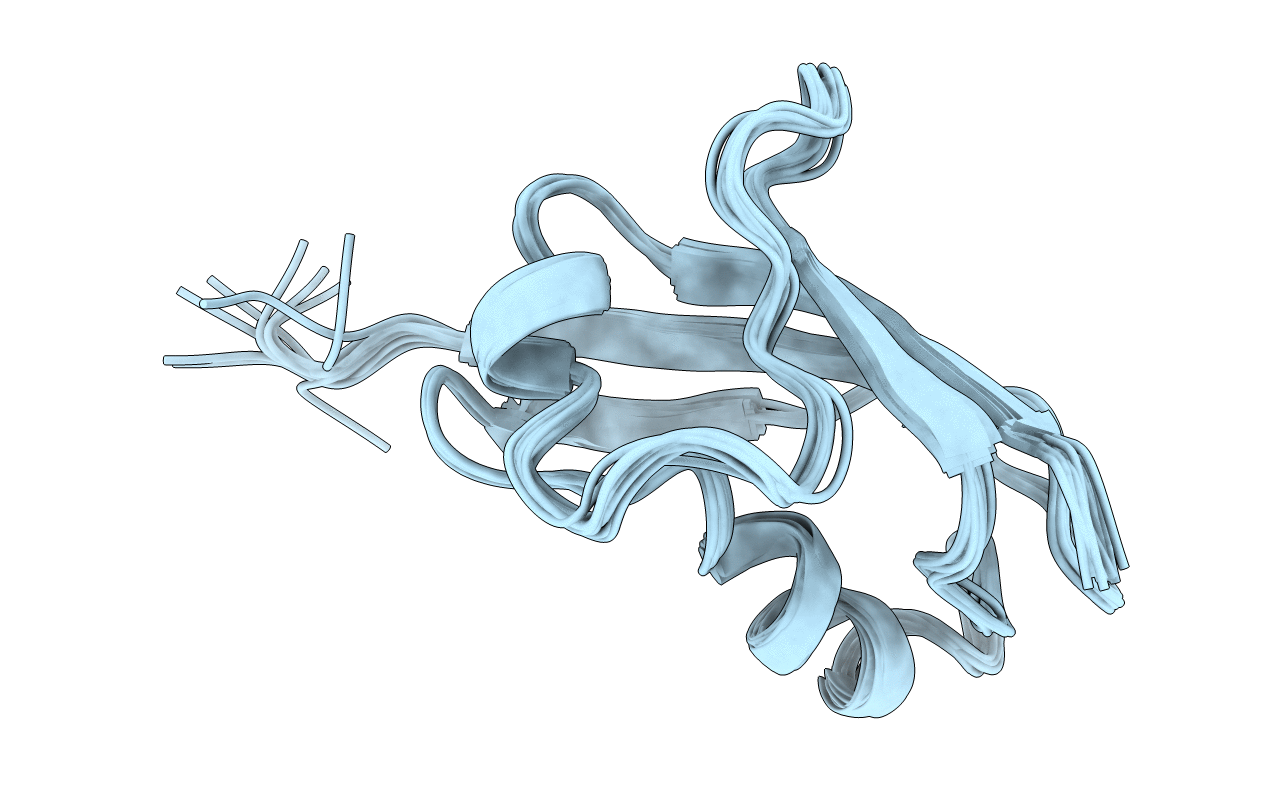
Deposition Date
1998-07-09
Release Date
1999-02-16
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1RLF
Keywords:
Title:
STRUCTURE DETERMINATION OF THE RAS-BINDING DOMAIN OF THE RAL-SPECIFIC GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE EXCHANGE FACTOR RLF, NMR, 10 STRUCTURES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
30
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
ENERGY