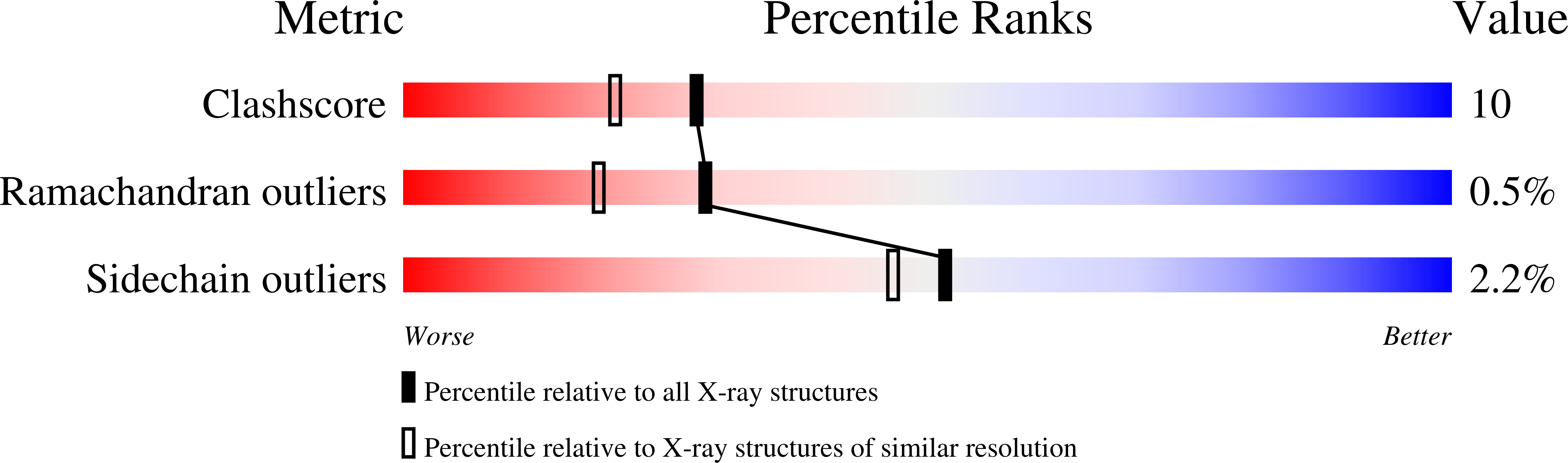Deposition Date
2003-11-20
Release Date
2004-12-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1RJY
Keywords:
Title:
Mhc Class I Natural Mutant H-2Kbm8 Heavy Chain Complexed With beta-2 Microglobulin and Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein B Peptide
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Herpes simplex virus (Taxon ID: 126283)
Herpes simplex virus (Taxon ID: 126283)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 1 21 1