Deposition Date
2003-11-14
Release Date
2004-03-30
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
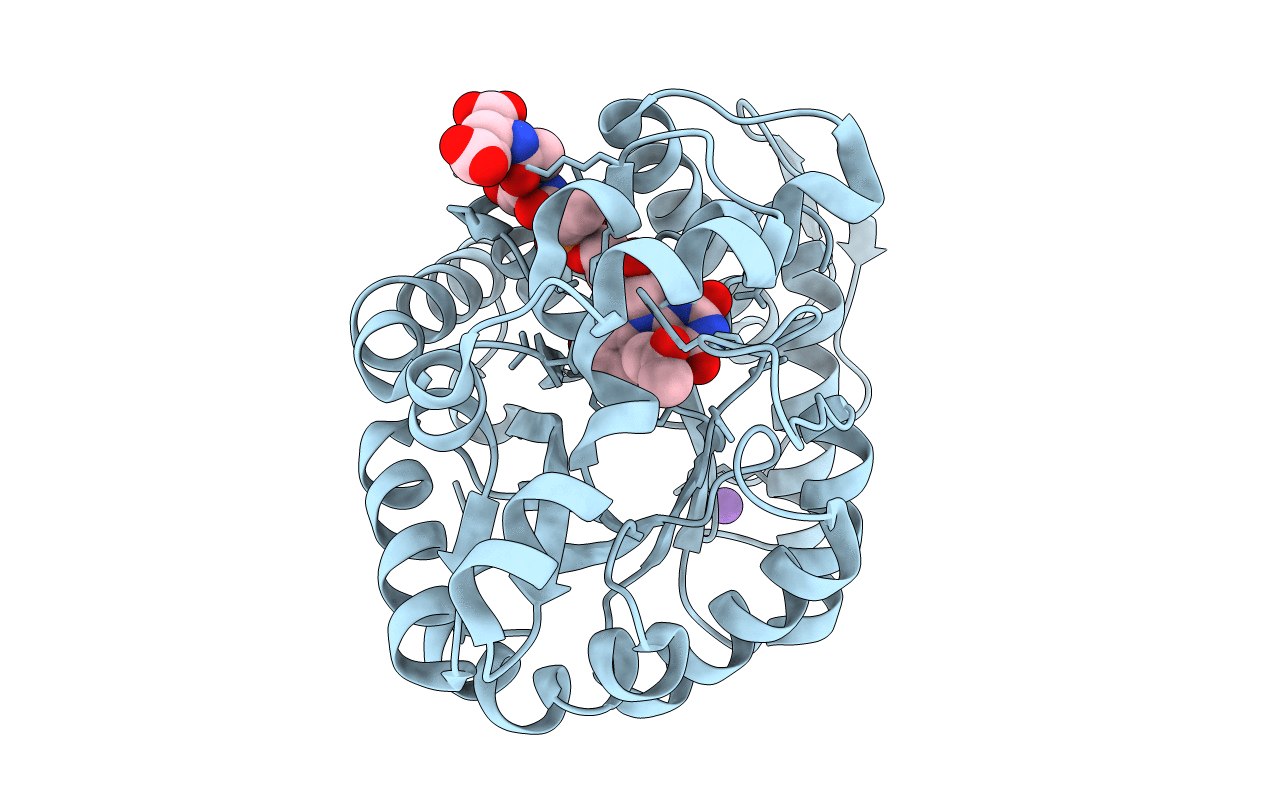
PDB ID:
1RHC
Keywords:
Title:
F420-dependent secondary alcohol dehydrogenase in complex with an F420-acetone adduct
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Methanoculleus thermophilus (Taxon ID: 2200)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.15
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
C 2 2 21


