Deposition Date
2003-10-13
Release Date
2004-05-25
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1R5T
Keywords:
Title:
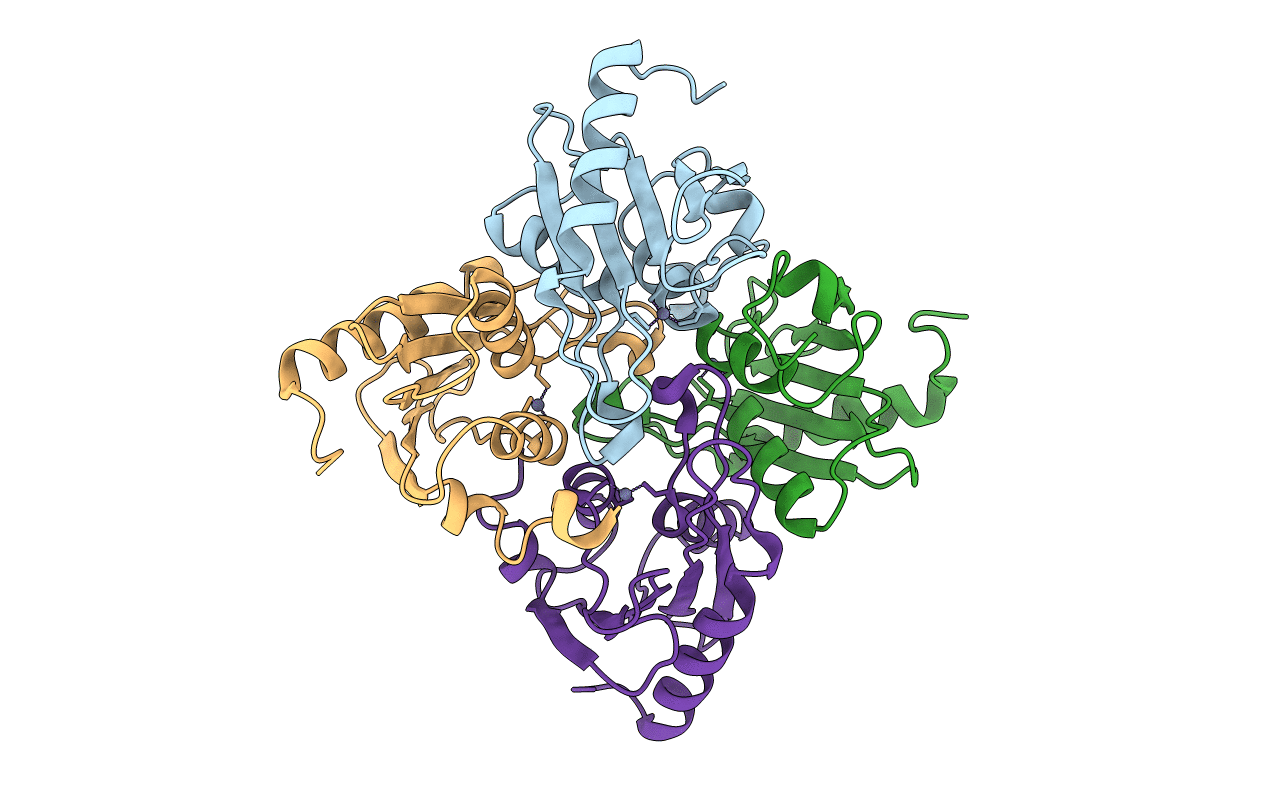
The Crystal Structure of Cytidine Deaminase CDD1, an Orphan C to U editase from Yeast
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
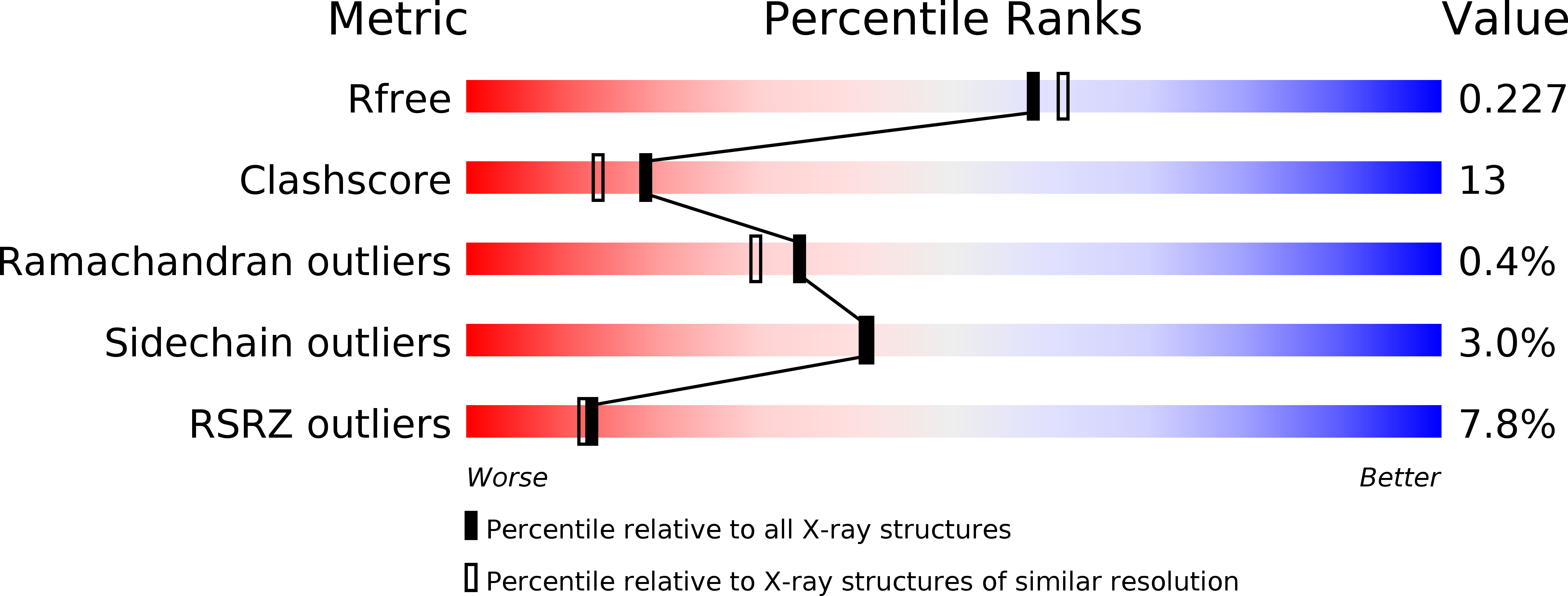
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
C 2 2 21