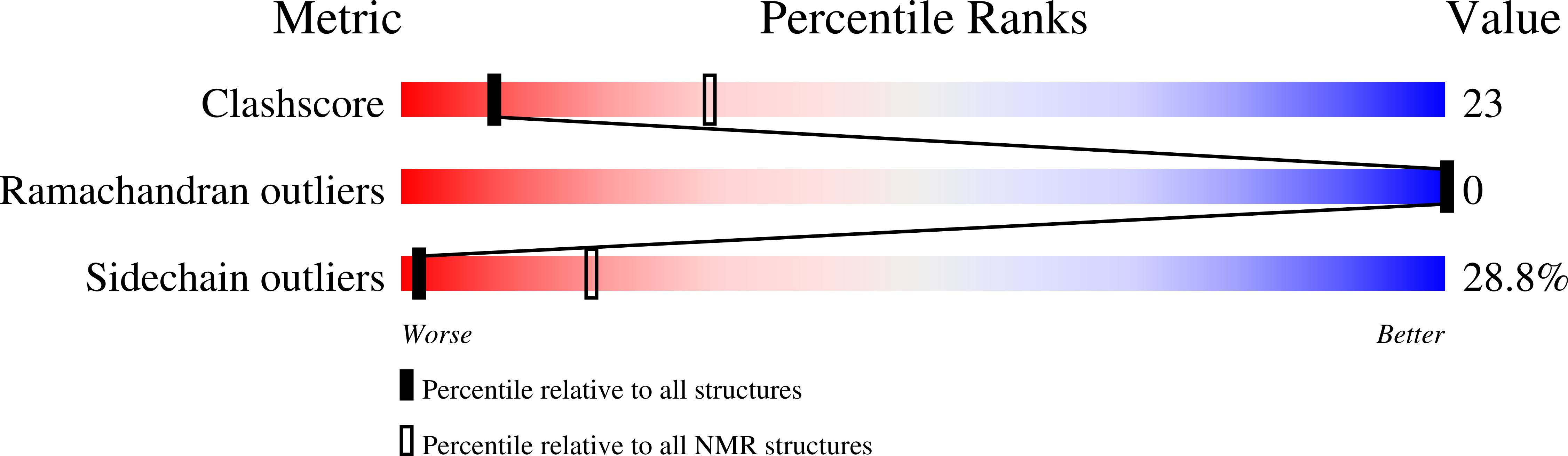
Deposition Date
2003-10-03
Release Date
2003-12-23
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1R48
Keywords:
Title:
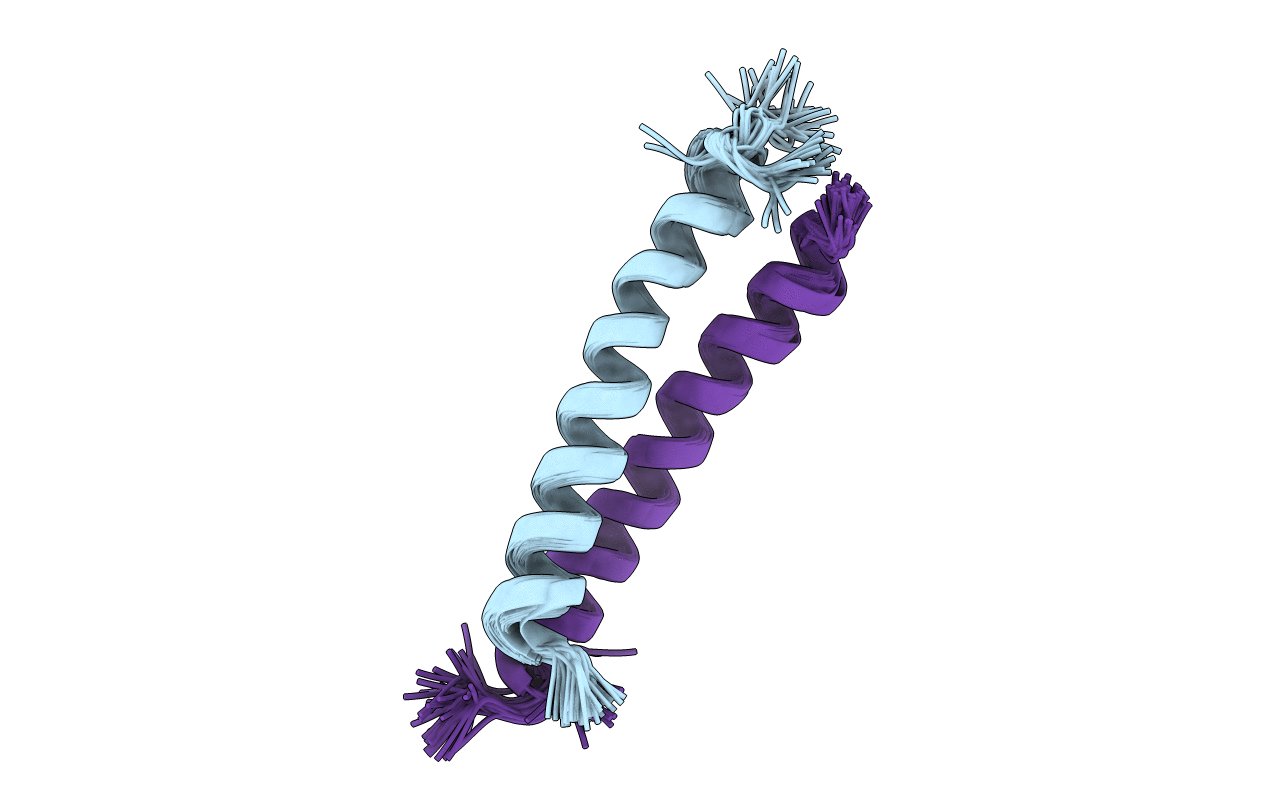
Solution structure of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain residues 468-497 of Escherichia coli protein ProP
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
63
Conformers Submitted:
51
Selection Criteria:
structures with favorable non-bond energy