Deposition Date
1995-11-11
Release Date
1996-07-11
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1QUL
Keywords:
Title:
PHOSPHATE-BINDING PROTEIN MUTANT WITH ASP 137 REPLACED BY THR COMPLEX WITH CHLORINE AND PHOSPHATE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
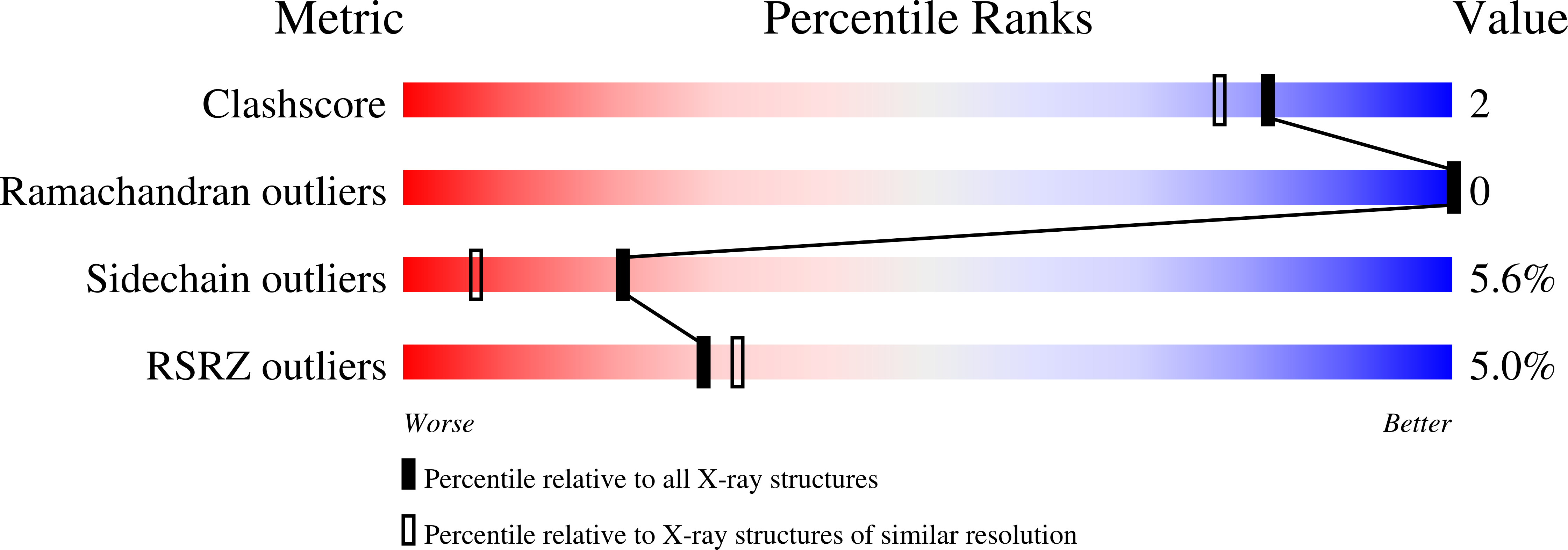
Resolution:
1.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21