Deposition Date
1999-07-30
Release Date
1999-10-24
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1QKP
Keywords:
Title:
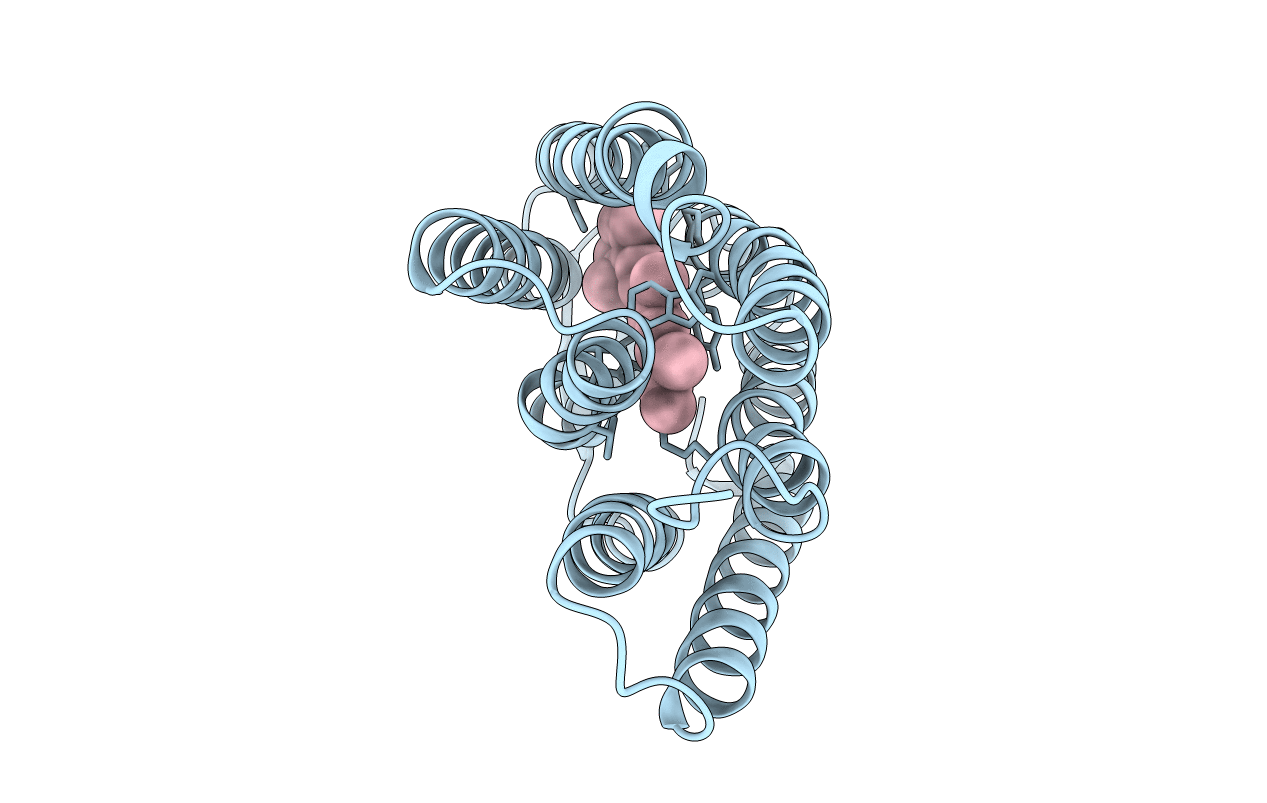
HIGH RESOLUTION X-RAY STRUCTURE OF AN EARLY INTERMEDIATE IN THE BACTERIORHODOPSIN PHOTOCYCLE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HALOBACTERIUM SALINARIUM (Taxon ID: 2242)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
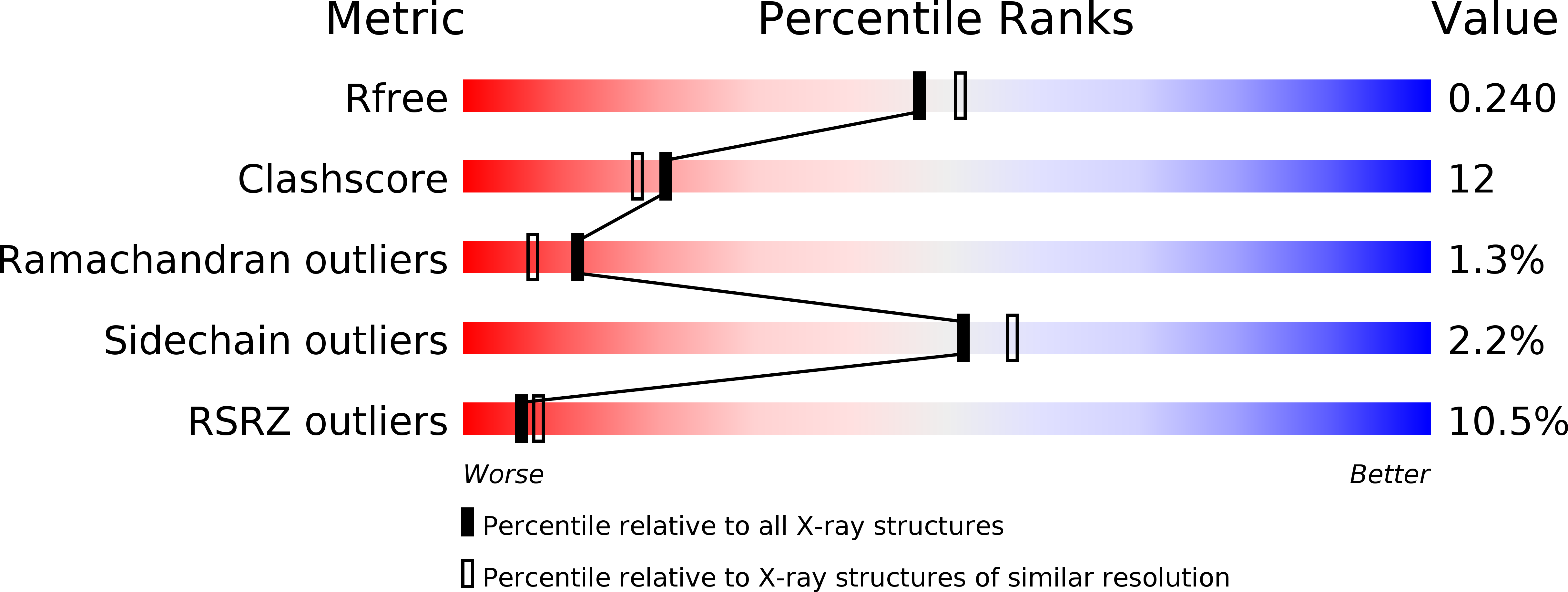
Resolution:
2.10 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 63