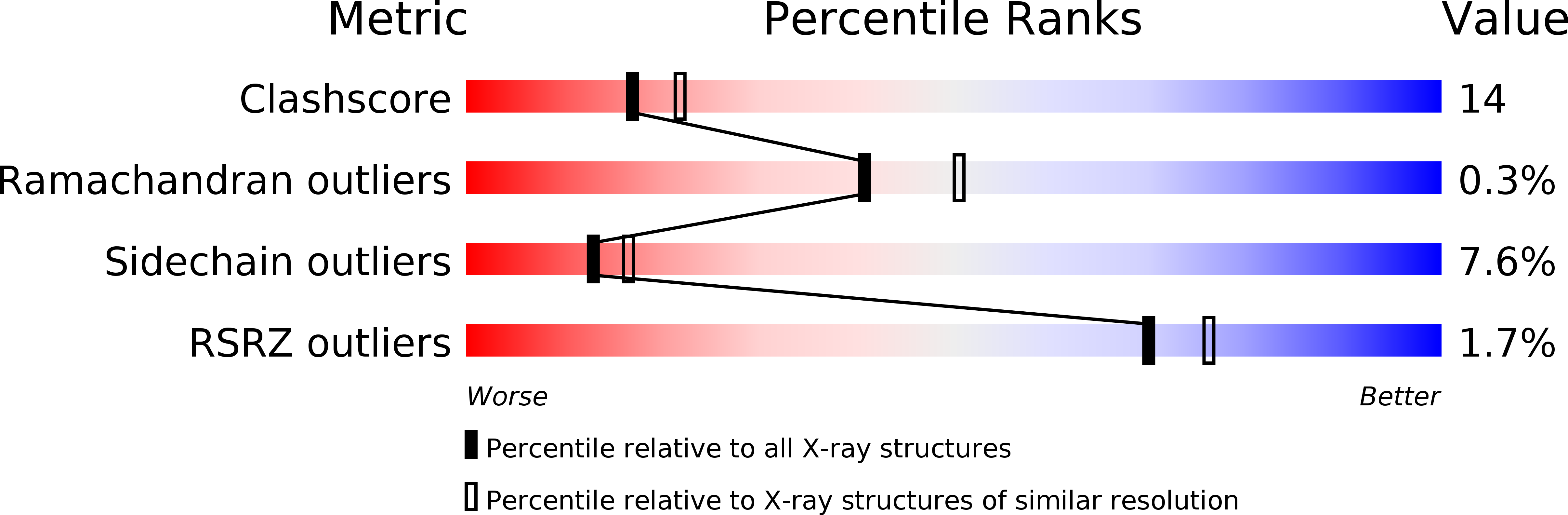
Deposition Date
1999-07-22
Release Date
1999-07-28
Last Version Date
2023-12-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1QKJ
Keywords:
Title:
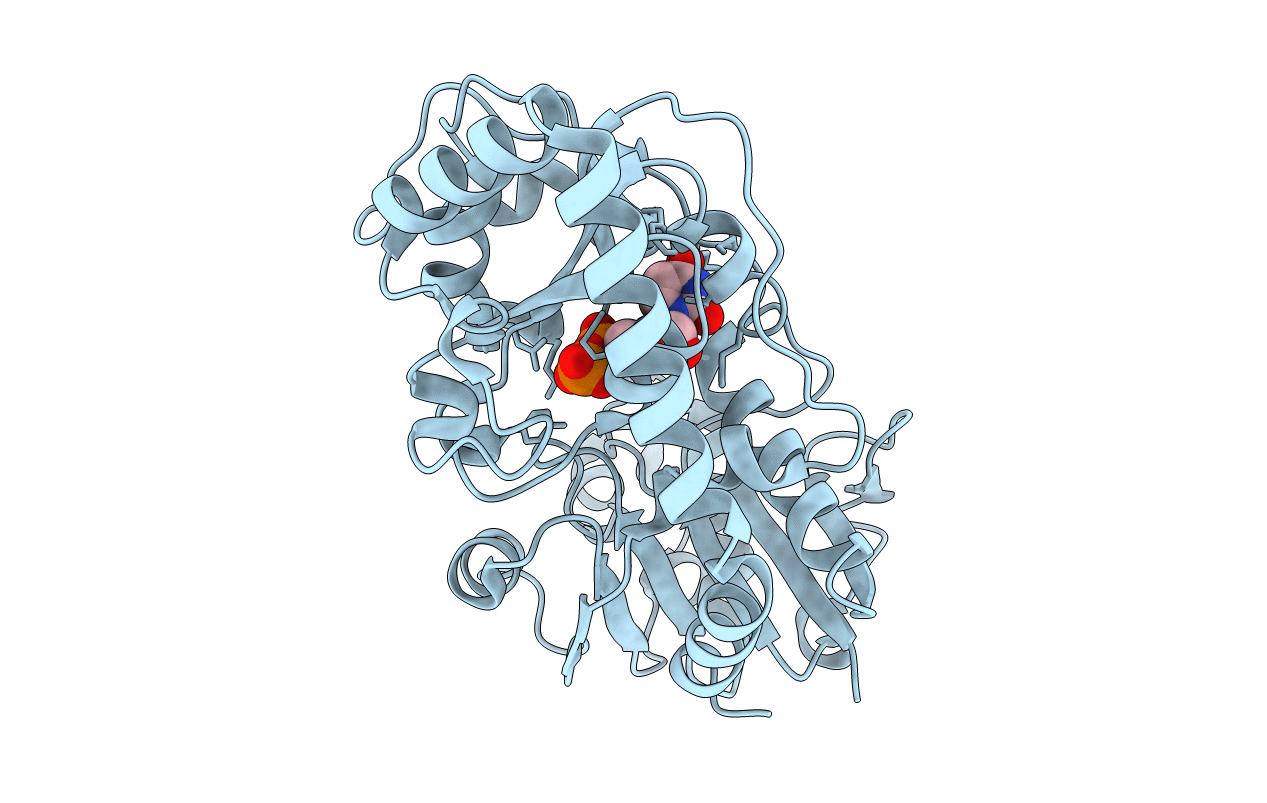
T4 Phage B-Glucosyltransferase, Substrate Binding and Proposed Catalytic Mechanism
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
BACTERIOPHAGE T4 (Taxon ID: 10665)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21