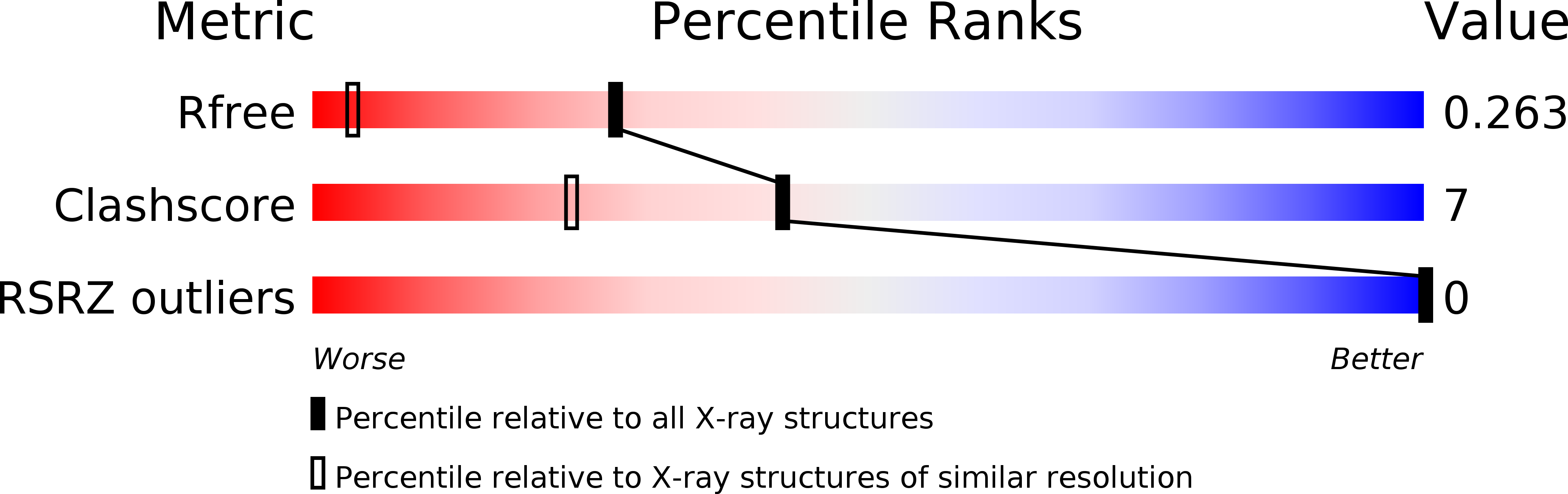
Deposition Date
2003-06-25
Release Date
2003-10-14
Last Version Date
2024-02-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1PUY
Keywords:
Title:
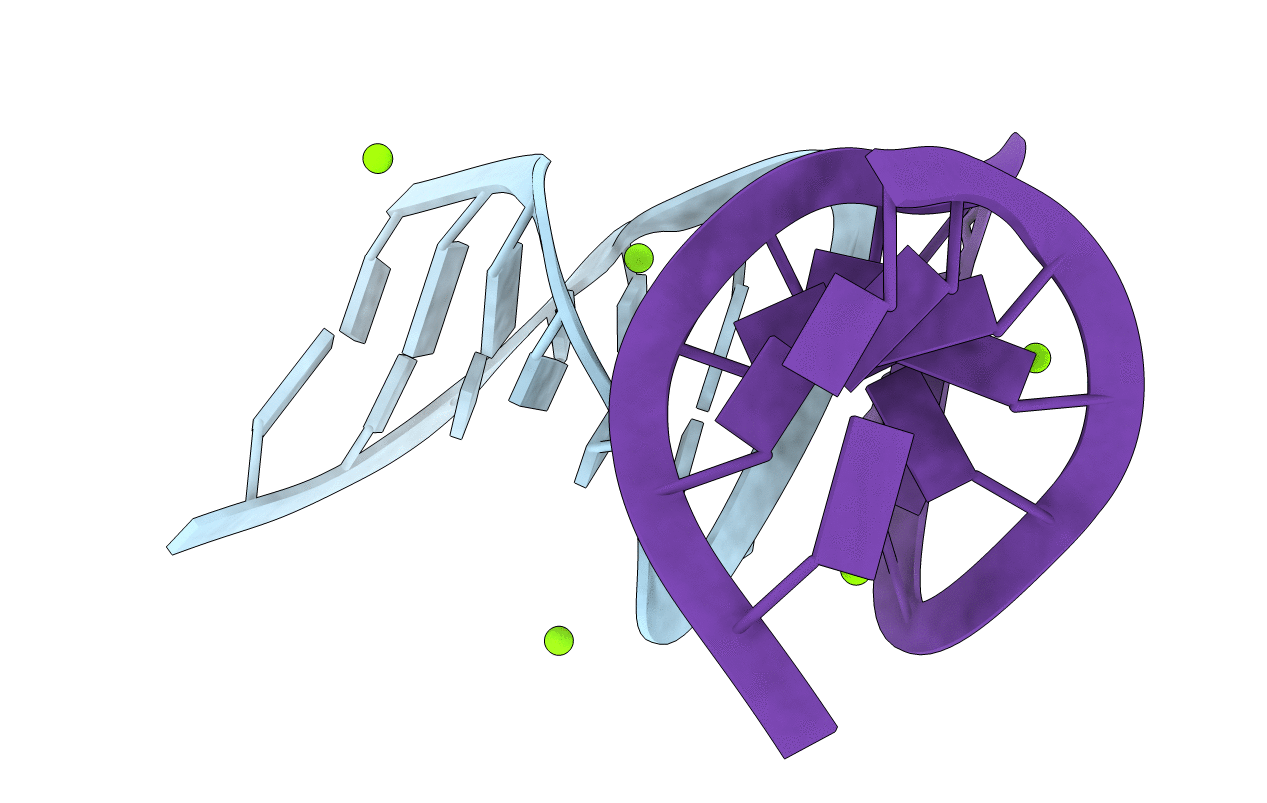
1.5 A resolution structure of a synthetic DNA hairpin with a stilbenediether linker
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 21 21 21