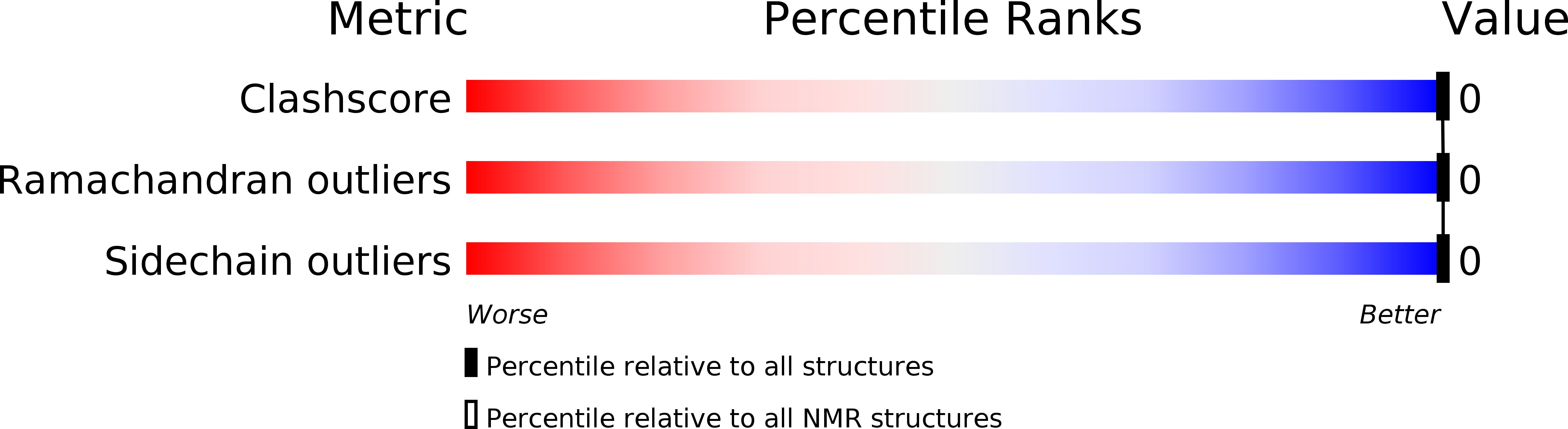
Deposition Date
1995-10-05
Release Date
1996-01-29
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1PAN
Keywords:
Title:
A COMPARISON OF NMR SOLUTION STRUCTURES OF THE RECEPTOR BINDING DOMAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA PILI STRAINS PAO, KB7, AND PAK: IMPLICATIONS FOR RECEPTOR BINDING AND SYNTHETIC VACCINE DESIGN
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 287)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
1