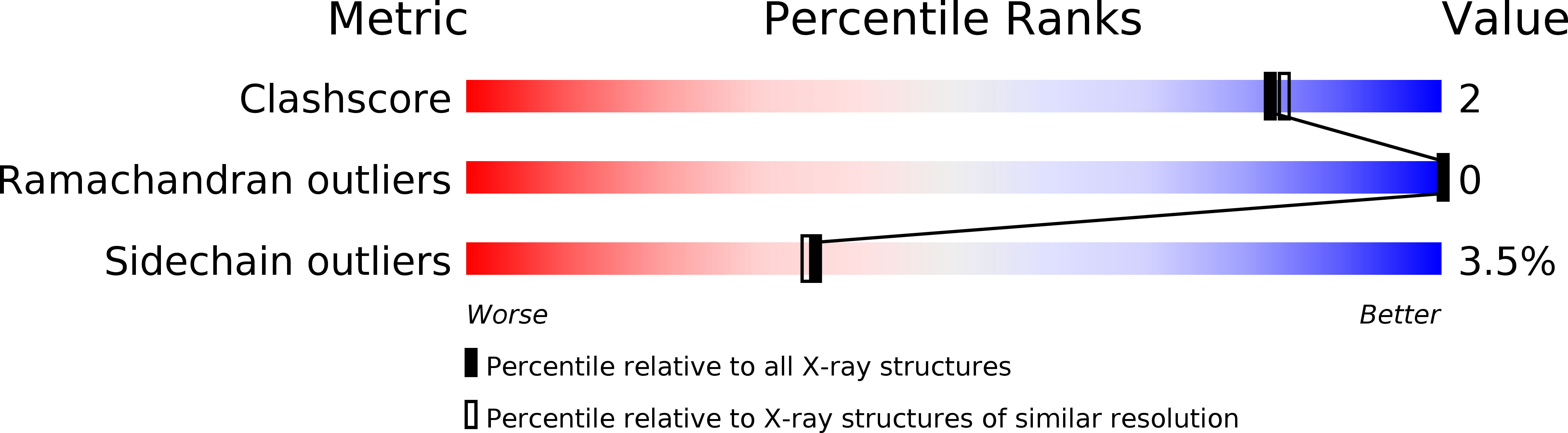Deposition Date
1989-04-24
Release Date
1990-04-15
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1P01
Keywords:
Title:
Serine protease mechanism. structure of an inhibitory complex oF ALPHA-LYTIC Protease and a tightly bound peptide boronic acid
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Lysobacter enzymogenes (Taxon ID: 69)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.13
Space Group:
P 32 2 1