Deposition Date
1994-06-13
Release Date
1995-01-26
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
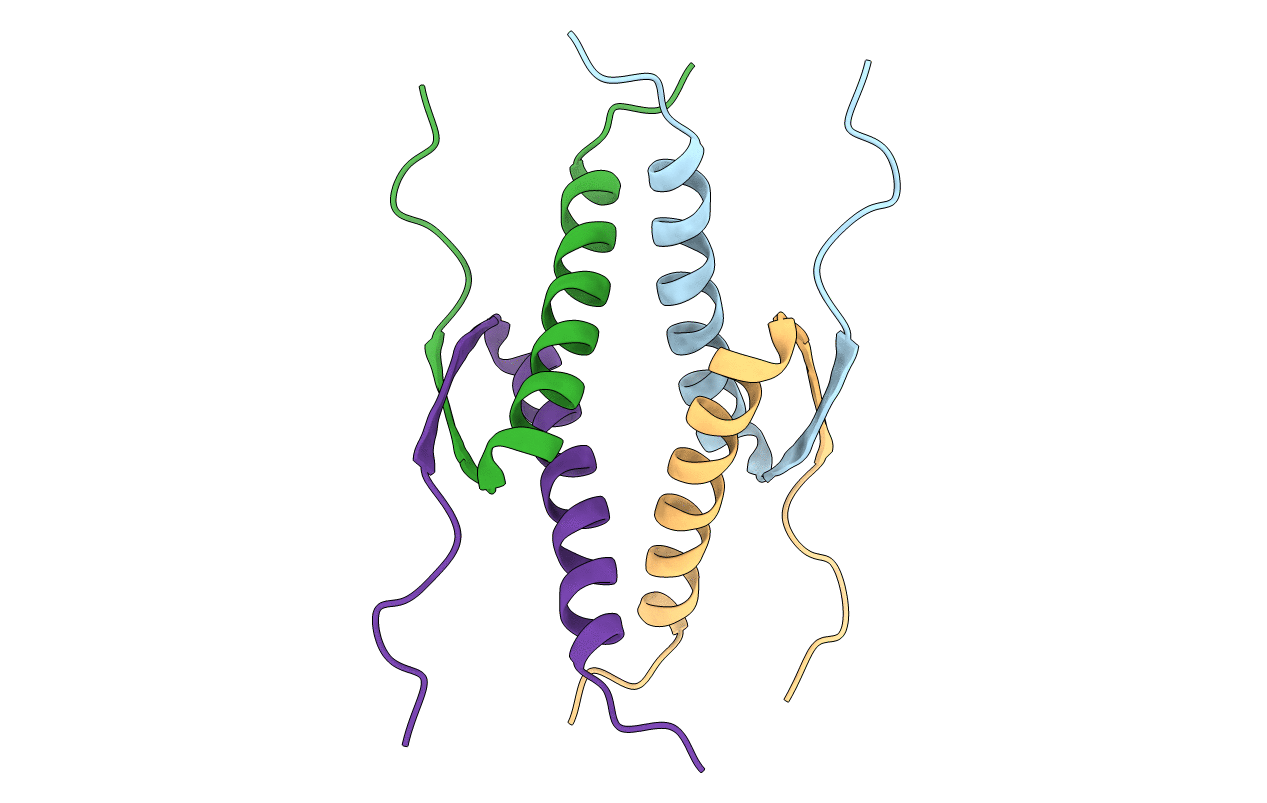
PDB ID:
1OLG
Keywords:
Title:
HIGH-RESOLUTION SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE OLIGOMERIZATION DOMAIN OF P53 BY MULTI-DIMENSIONAL NMR
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Submitted:
1


